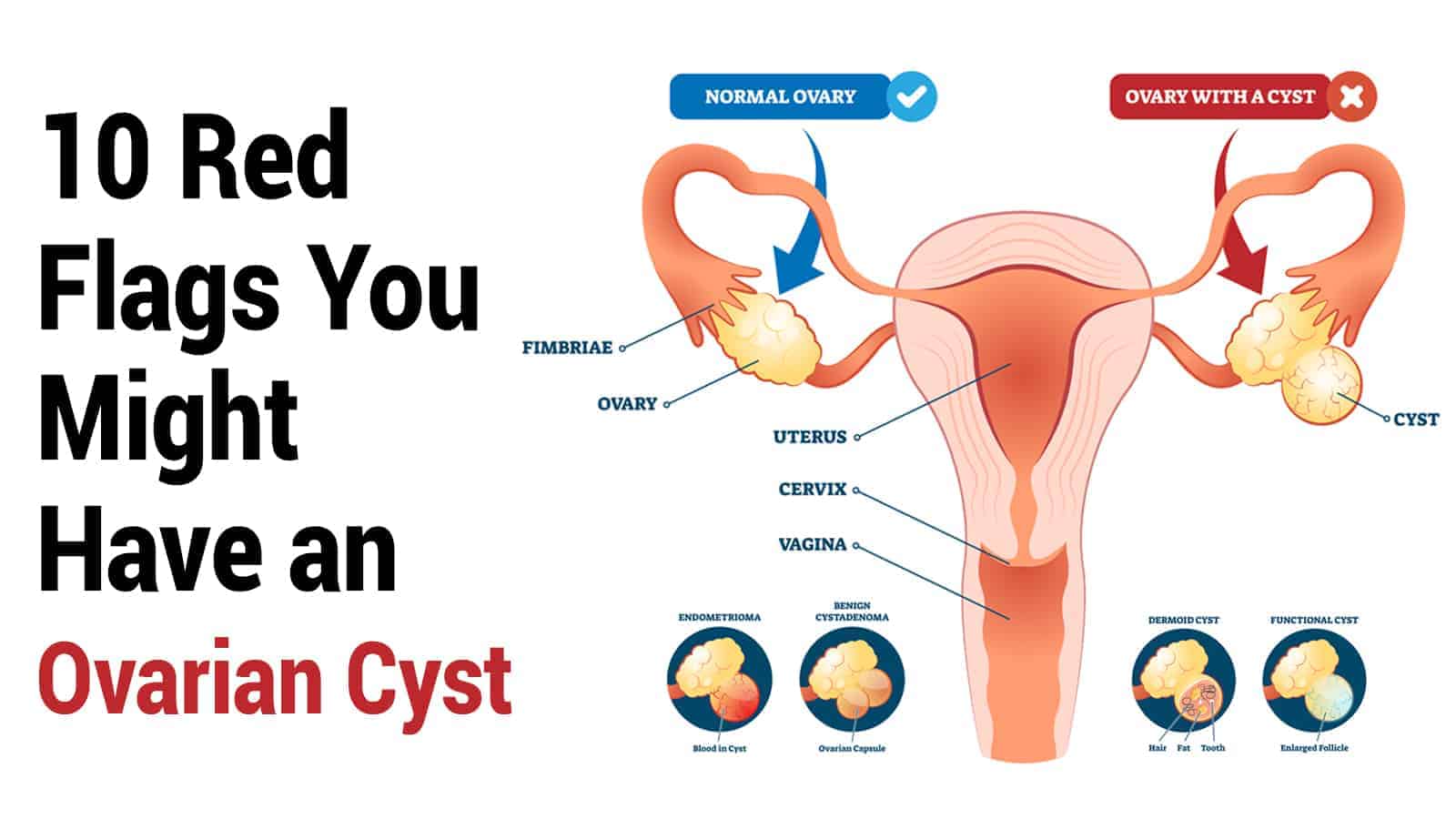
Ovarian cysts form in or on a female’s ovaries as fluid-filled sacs. Most of the time, they are painless and cancer-free. However, they also make their presence known from time to time and cause trouble for other women. If you’re curious to know if you have an ovarian cyst, here are 10 red flags that could indicate you have one.
What are ovarian cysts?
Studies show that approximately 10 out of every 100 women suffer from ovarian cysts. About the size of a small berry, ovarian cysts that grow during hormonal changes such as puberty or menopause are called functional cysts. They can develop in one or both of your ovaries.
The most common functional ovarian cysts include the following:
 Follicular cysts
Follicular cysts
These cysts form when the follicle or capsule that surrounds the egg hinders the release of the egg. The follicle fills with fluid and turns into a cyst.
Corpus luteum cyst
The corpus luteum secretes progesterone and estrogen. It fills with blood when the follicle releases the egg.
Theca lutein cyst
These cysts form in women who are getting infertility treatments using hormones. The fertility hormones stimulate egg cell growth in your ovaries, but these cysts may form as a side effect.
Chocolate cysts
These cysts are filled with thick, dark blood. They form because of endometriosis.
Polycystic ovary syndrome
These are several small cysts that grow in your ovaries. PCOS occurs when you have too much androgen (male sex hormones), which prevents your eggs from growing and maturing.
What do ovarian cysts look like?
These cysts are anywhere from one to three centimeters. They usually go away on their own. Complications are rare, but sometimes the wall of the cyst ruptures, causing fluid to leak out. This may be painful, but it rarely needs treatment or surgery since it will eventually dissolve.
Signs you might have an ovarian cyst
1 – Menstrual cycle problems
Ovarian cysts can cause heavy or irregular periods or spotting. You get these menstrual cycle problems if the ovarian cyst produces too many sex hormones so that the lining of your womb starts to grow.
2 – Pain in your lower abdomen
Your pain may feel dull and constant. Sometimes ovarian cysts rupture or they cause a twist, which is especially painful. You may also feel heaviness in your lower abdomen too.
3 – Swollen stomach
Sometimes, ovarian cysts grow large and cause bloating due to fluid retention due to your body’s inflammatory response. You may feel discomfort from pressure around your stomach area.
4 – Sudden pain
If the weight of the cyst pulls on the ovary, it can become twisted. This can be very painful. You may feel severe cramping in your lower abdomen. Some women have nausea, a faster heart rate, and even vomiting. If you have these symptoms, call your doctor immediately.
5 – Pain during intercourse
Ovarian cysts can make it painful to have intercourse. This is because, during intercourse, the ovaries are touched and can begin to leak fluid. This is most common if you have endometriosis. Talk to your OB/GYN about this pain. They can give you some suggestions on how to avoid painful intercourse.
6 – Breast tenderness
When an ovarian cyst grows, it releases hormones in your body. The hormones cause fluctuations, which makes your breast tissue to feel tender and sore. One accidental bump to your chest can send you through the roof with pain in your breasts. If you’re experiencing this, be sure to mention it to your OB/GYN. In the meantime, try to find relief with a heating pad or acetaminophen to ease the pain.
7 – Urinary tract problems
If your ovarian cyst gets too large, it presses against your urinary tract system, which can cause problems. You’ll feel pressure in your bladder, making you feel like you need to pee a lot. Or you may have trouble peeing. Be sure to mention these symptoms to your OB/GYN. They can do an exam to see if you have a cyst. Large cysts can also cause constipation.
8 – Leg and hip pain
Leg and hip pain isn’t usually associated with an ovarian cyst, but it’s more common than you think. Ovarian cysts can put pressure on your pelvic nerves, which in turn causes pain in your hip or leg region. The pain is usually only on one side. You may feel the pain move to your groin or abdomen area. If it bursts, it will be excruciating. Be sure to mention your hip or leg pain to your OB/GYN. They are familiar with ovarian cyst symptoms, so they can examine to determine if a cyst is the cause of pain.
9 – Loss of appetite
When you have an ovarian cyst, you may lose your appetite. This could be due to pressure on your abdomen area, making you feel full and bloated. Plus, the hormonal fluctuations from an ovarian cyst can also take away your appetite. Many women lose weight. If you’re losing weight and not trying to, talk to your doctor about your fullness, pain, or bloated feelings.
10 – Pain in the lower back
This red flag often gets misinterpreted as something else besides an ovarian cyst. You may think you’ve been working out too much at the gym, but if the pain in your lower back persists, you might have an ovarian cyst. As the cyst fills with fluid, they put pressure on your abdomen, upsetting your menstrual cycle due to hormonal changes, which may cause a dull aching feeling in your lower back.
 What if an ovarian cyst is a cancer?
What if an ovarian cyst is a cancer?
This is a type of cancer that grows in your ovaries. This type of cancer is the 5th most common cancer in women. It causes more deaths in women than any other type of reproductive type of cancer. There’s no clear cause of ovarian cancer. You’re at risk of ovarian cancer for many reasons. You’re a higher risk if
- You have fewer kids, and you give birth later in life.
- You had breast cancer or have a family history of breast cancer or ovarian cancer.
- If you take estrogen replacement for more than 5 years.
- You’re older. Most deaths occur in women 55 years and older.
Ovarian cancer symptoms are sometimes hard to see. Oftentimes, you think your symptoms are due to something else. So by the time it’s finally diagnosed, cancer has spread. But, if you have these symptoms even for a few weeks, talk with your doctor.
- Swollen belly, feeling bloated.
- You feel full all the time. Many people don’t really want to eat.
- Pelvic pain or low abdomen pain
- Back pain
- Swollen lymph nodes in your groin area.
- Excessive hair growth. The hair is dark and coarse.
- You need to urinate all of a sudden, with little warning.
- You need to urinate all the time.
- Constipation
How do doctors diagnose ovarian cysts?
If you think you may have an ovarian cyst, make an appointment with your OB/GYN. They will do a pelvic exam. They sometimes can feel the cyst. Some women don’t realize they have a cyst until they have a pelvic exam. If your doctor finds a cyst, they will do some tests to know more about it. The tests usually include
1 – Ultrasound
An ultrasound can determine the size, location, and shape of the cyst. It will also tell your doctor whether the cyst is solid or filled with fluid.
2 – MRI
An MRI will help your doctor see more details of the cyst.
3 – Pregnancy test
Your doctor will do a pregnancy test to see if you’re pregnant because this may be the cause of your cyst.
4 – Blood tests
Blood tests help reveal hormonal fluctuations or problems. This will also determine whether the cyst is bleeding.
5 – Biopsy
If necessary, a small piece of the cyst is removed and examined more closely. They are looking for cancer cells.
How do doctors treat ovarian cysts?
Treatment of the cyst depends on what type it is, your age, and your overall health. Most of the time, no treatment is necessary. Your doctor may tell you to keep an eye on your symptoms. The cyst will probably go away over a few weeks. Doctors don’t do surgery unless you have excessive pain, pressure, or it seems to be growing.
 Final thoughts on dealing with an ovarian cyst
Final thoughts on dealing with an ovarian cyst
Ovarian cysts are prevalent in women. Most women will have one or more in their lifetime. Typically, they don’t cause problems, but there will be some uncomfortable symptoms once in a while. Common symptoms range from feeling bloated, pressure in your abdomen to difficulty urinating or pain during intercourse. Strange symptoms like back pain or leg pain are not that unusual when you have an ovarian cyst. Of course, loss of appetite or sudden severe pain should be mentioned to your doctor right away. Ovarian cancer is a real threat to women, especially older women.
If you have a history of breast or ovarian cancer in your family, tell your OB/GYN so they can check for symptoms early on. Staying educated about ovarian cysts is important for all women to understand their bodies and know what is and isn’t normal.