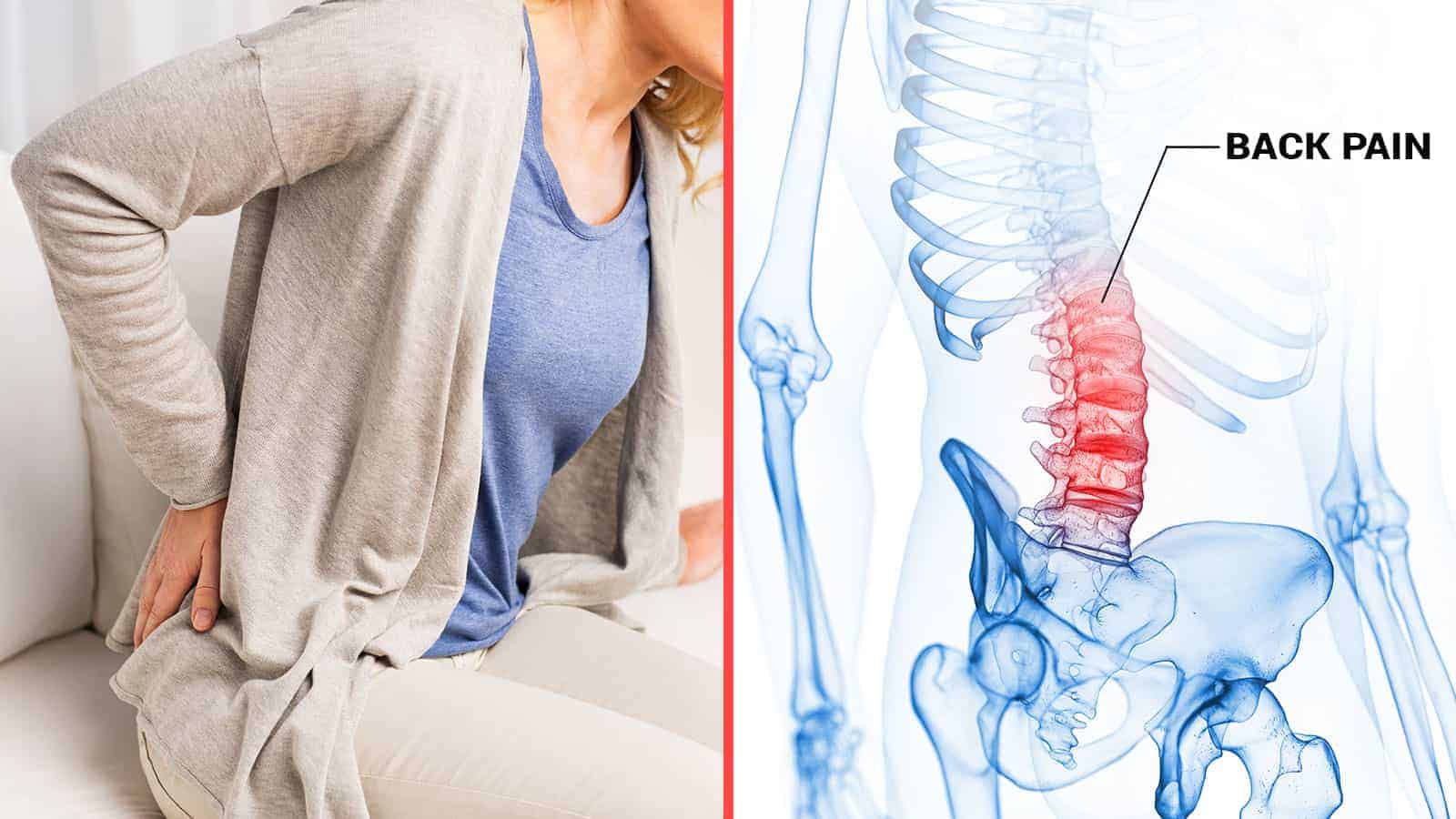
Anybody who has ever experienced back pain knows that it’s no joking matter.
Per the American Chiropractic Association, back pain is the number one cause of disability around the globe. In the United States, 80 million working adults experience the discomfort of the back or neck every year, resulting in a total of more than 260 million days of work missed.
Here are some other facts about this painful condition:
– 80% of people experience an aching or painful back at some time in their lives.
– Backaches are the 3rd most common reason for doctor visits.
– Back issues costs Americans up to $100 billion annually.
– Most causes of spinal discomfort are caused not by a medical condition, but an alteration of the back’s physiology (e.g., a degenerative or herniated disc.)
– The number of disabled due to problems with the lower back has risen 54% between 1990 and 2015.
– Back (and neck) pain, if left untreated, can progress into a chronic and debilitating medical condition. For the vast majority of such cases, the resultant symptoms are wholly preventable.
While back pain is quite common, and its symptoms uncomfortable, spinal pain is rarely severe. However, there are exceptions. In this article, we’re going to describe seven signs that your back pain may be more serious than you think. We’ll also discuss the causes, symptoms, and risk factors associated with back pain.
Let’s do this!
Causes, Symptoms, and Risk Factors
Causes of back pain
Spinal pain is classified into acute and chronic causes. Acute causes of back discomfort include heavy lifting, a fall, or a blow to the back. Please note that acute causes of back pain should always be examined by a doctor. Acute bouts of these symptoms usually lasts no longer than six weeks.
Chronic back pain is that which exceeds three months in duration. This diagnosis is far less common than the acute variety. Medical conditions and event s that may trigger back pain include:
– Arthritis. Osteoarthritis can induce lower backaches or pains. A condition known as spinal stenosis involves the narrowing of the space around the spinal cord. Spinal stenosis can trigger severe spinal pain.
– Herniated or Ruptured (“Slipped”) disks. Spinal disks cushion the vertebra by acting as a kind of “shock absorber” of the spine. Disc degeneration (caused most often by aging) causes these discs to stiffen, which may lead to a herniated or ruptured disc. When either occurs, either the disk or disk material places pressure on nearby nerves, which may trigger back pain.
– Ligament or muscle strain. Repeated heavy lifting, repetitious movements, or a sudden awkward movement may cause posterior ligaments or muscles to strain.
– Osteoporosis. Bones that are brittle and porous may cause the bones in the back to compress. This compression is commonly linked to back pain.
– Scoliosis. Scoliosis is an unnatural curvature of the spine. The condition may lead to middle-age pain in the spine, from the neck to the lower back.
Symptoms of Back Pain
Common signs and symptoms of the condition are as follows:
– Arm or leg pain
– Loss of mobility
– Muscle ache
– Muscle weakness
– Numbness or tingling
– Pain that is reduced by reclining
– Radiating pain that travels down the leg
– Shooting or sharp pain
– Worsening pain caused by bending, lifting, standing, walking or running
Risk factors
Here are some of the common factors that increase the risk of back pain:
– Aging. Back pain is more common as we get older, starting at around age 30 or 40.
– Excess weight. Too much weight puts undue stress on your back, which may lead to medical complications and/or back pain.
– Lack of exercise. Abdominal and back muscles that aren’t used may cause tenderness. Such often occurs due to a lack of exercise.
– Job-related conditions or hazards. Occupations that require heavy lifting, forceful bodily contact, or contortion may lead to back problems or discomfort.
– Psychological conditions. Anxiety and depression may increase one’s susceptibility to back pain.
– Poor posture. Slouching puts a disproportional amount of pressure on specific areas of the back, leading to pain and discomfort. Sleeping in awkward positions may also result in acute back pain symptoms.
– Sedentary lifestyle. Unfortunately, much of the developed world lives an inactive lifestyle. Lack of movement can cause bodily pains, including those of the back.
– Smoking. Cigarette smoke disrupts blood flow to the spine. As a result, sufficient nutrients from food may not be regularly available. Either or both can trigger or worsen back pain symptoms.
7 Signs Back Pain Is Something More Serious
Here are 7 signs that your back pain may be something more serious than initially thought.
The pain is persistent
If your discomfort remains active for more than a few days or requires the constant use of pain medicine, it’s advisable to be seen by a doctor. Continuous pressure around the sensitive nerves can cause fluid buildup. In turn, the nerves can become permanently damaged. Additional symptoms, such as worsened pain, scarring, and swelling, may also arise.
In time, severe spinal pain can impose lifestyle limitations. It may become challenging to do light activity, including what were once enjoyable activities.
Eventually, long-term pressure on the neck may also induce neck pain and vice-versa. Other severe conditions that may result from severe uncorrected back pain include cervical arthritis, headaches, respiratory complications, and vertebral bone spurs.
If your back pain was caused by a slip and fall accident caused by someone else’s negligence, you may need to search for ‘slip and fall lawyers near me’ online.
You were in a car accident
We’ve probably all be there: we’re in a minor fender-bender or some small impact car accident. We may feel a bit jarred, but our body feels fine. So we just continue on. In most cases, things turn out okay. However, it is important to know that a seemingly small injury can indeed worsen over time’ especially injuries to the neck or back.
Conditions that may arise from a car accident include:
– Back and neck injuries: including disc injuries, spine injuries, fractures, and sprains
– Soft tissue injuries: including bruising, sprains, and tearing; torn ligaments, muscles, and tendons.
– Whiplash: symptoms include back and neck pain, headaches, and tinnitus (a “ringing” or “beating” sound in the ears without a stimulus.)
It is therefore recommended that if you’re in a car accident and you feel any pain that you are checked out by a doctor. Ignoring back pain can lead to serious – and often unnecessary – complications. Additionally, consulting a personal injury lawyer from a reputable firm like Cambre & Associates can help you understand your rights and seek the compensation you deserve.
Injured in New York? Call a New York personal injury lawyer from Cellino Law. Consult a cincinnati rear end accident attorney if you have just been rear-ended by a negligent driver.
There’s a pain in your side
Oh, boy. Has anyone reading this ever had a kidney stone? If you have, you’re well aware of the agony – and the frustration of getting rid of it.
Which brings us to the next point. If you feel a sharp pain in the upper back and on your side, you should get checked out. Kidney stones often manifest these symptoms. Other possible signs of kidney stones: discomfort or tenderness while peeing, or brown- or red-hued urine. If you feel pain below the shoulder blades, you may have an issue with your gallbladder and should be seen by a doctor.
There’s a pain in your chest
Spinal pain accompanied by pain in the chest can signify a severe condition such as a stroke. Long-term high blood pressure (hypertension) may be the root cause. Another symptom to look out for is numbness in the arms.
In any case, pain in the chest is not something with which to mess around. Heart problems, though more common amongst the elderly, affects every age group. You should consider any combination of the symptoms above a medical emergency.
Do not wait to seek treatment, call 911.
You feel very fatigued
In one eye-opening survey, 43 percent of Americans admitted to being “too tired to function at work.” The National Safety Council also found that 97 percent (!) of survey respondents reported at least one risk factor for fatigue.
In short, Americans (and presumably the rest of the world) are all too familiar with fatigue and exhaustion. Unfortunately, the ubiquitous nature of fatigue is precisely why the problem is so overlooked – even if there’s a potential medical emergency. For example, a backache coupled with extreme fatigue, shortness of breath, and nausea could signify heart problems.
The symptoms mentioned above should also be considered a medical emergency.
A weakness of the legs
If, after lifting something heavy, you feel that discomfort accompanied by weakness or numbness of the legs, you could have a herniated disc. Herniated discs, also commonly referred to as “slipped discs” or a “slipped disc” can lead to severe complications if left untreated.
The discomfort of the upper back and neck and weakness of the legs also links to arthritis.
Pain while breathing or shortness of breath
And upper backache that’s accompanied by shortness of breath or discomfort while breathing may be indicative of a respiratory problem.
Punctured lung caused by an injury often produces these symptoms. In any case, a physical examination at minimum is necessary.
 Final Thoughts: Recognize When Back Pain is a Significant Problem
Final Thoughts: Recognize When Back Pain is a Significant Problem
Here are some indications that you should visit a doctor, per the Mayo Clinic:
– The discomfort is caused by a blow, fall, or some other sudden event.
– Your discomfort accompanies bladder or bowel difficulties
– The presence of a persistent and worsening fever.
– The discomfort is accompanied by unexplained weight loss.
Seek medical advice from your doctor when you have back pain. They will issue the diagnosis that will offer you the relief you need.