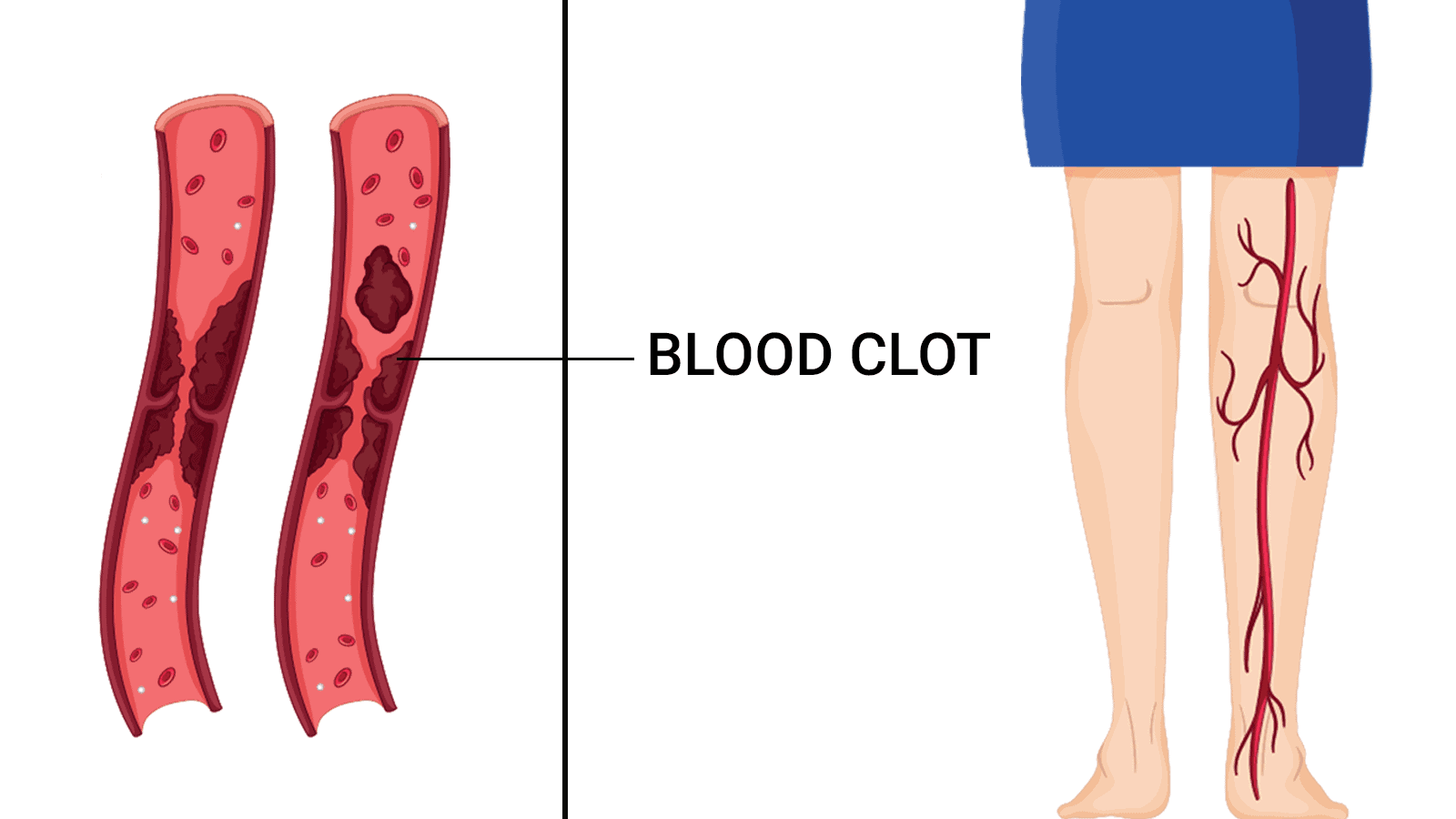
Blood clots are your body’s built-in repair system—a natural response to injury. When you get a cut, your blood thickens to stop the bleeding and begin the healing process. Sounds helpful, right? It is—until it forms where it shouldn’t. When a clot develops inside a vein, it can disrupt circulation, leading to serious blood clot symptoms that often go unnoticed. Understanding these early warning signs can distinguish between a manageable condition and a life-threatening emergency.
Sometimes, clots form when they’re not needed—deep inside veins, restricting blood flow. This is where things turn dangerous. When a clot develops in the deep veins of the legs (Deep Vein Thrombosis, or DVT), it can lead to swelling, pain, and serious complications. Worse? If that clot breaks loose and travels to the lungs (Pulmonary Embolism, or PE), it can block oxygen supply—sometimes fatally.
These conditions often develop silently, with symptoms mistaken for minor discomfort. But the sooner you recognize the red flags, the better your chances of preventing a life-threatening emergency.
What Causes Blood Clots?
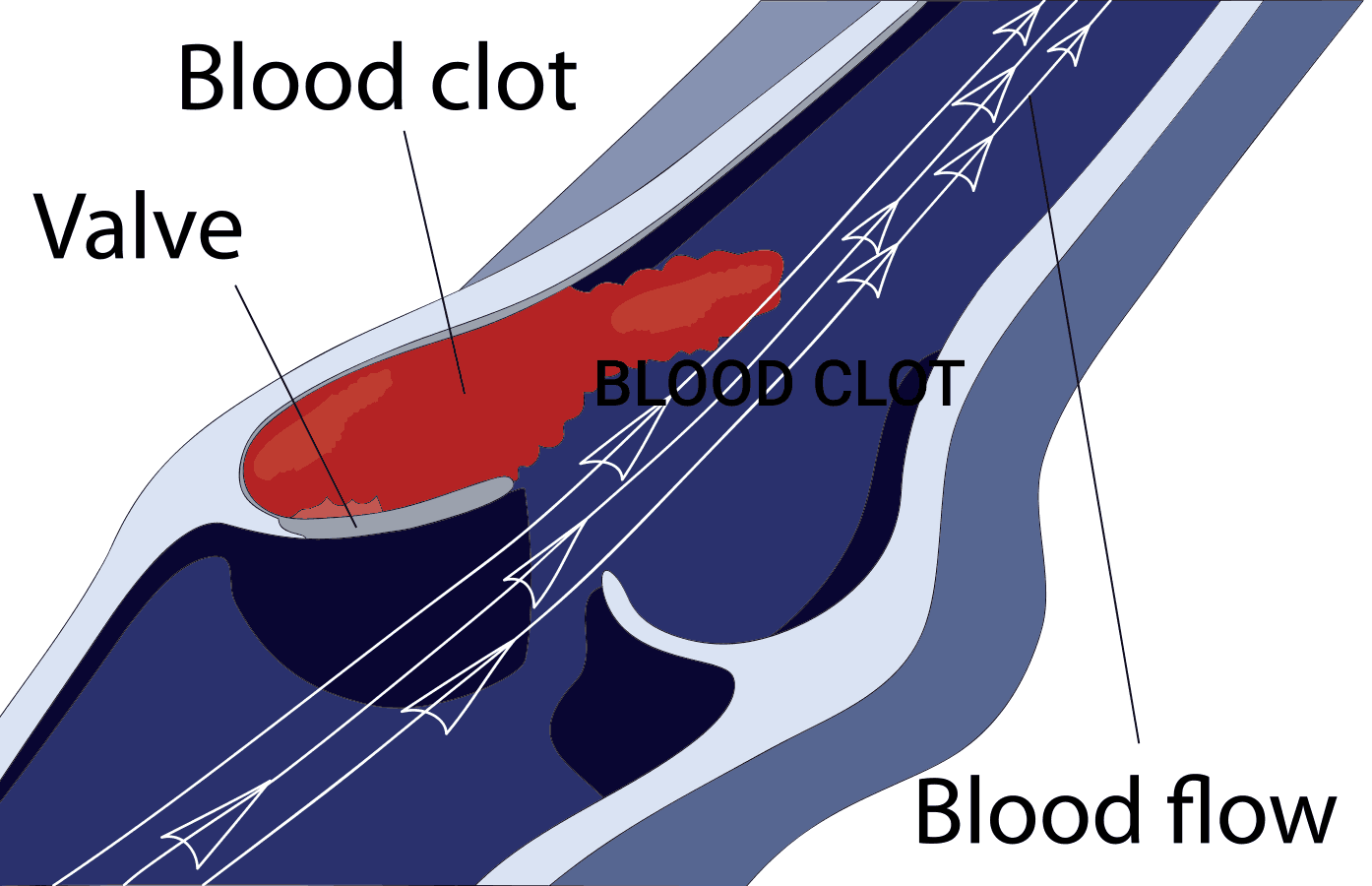
Blood clots don’t just appear randomly—they develop when something disrupts normal blood flow or triggers excessive clotting. While clotting is essential for healing wounds, an unnecessary clot inside a vein can become a silent but deadly threat.
Factors That Increase Blood Clot Risk
- Prolonged Inactivity & Immobility – Sitting for long periods slows circulation, increasing the chance of clot formation. Whether it’s a long-haul flight, post-surgery recovery, or bed rest due to illness, reduced movement allows blood to pool, making clotting more likely.
- Surgery & Underlying Medical Conditions – Major surgeries, especially those involving the abdomen, pelvis, or legs, can damage blood vessels and increase clotting risk. Conditions like heart disease, cancer, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders also make blood more prone to clotting.
- Genetics & Blood Disorders – If blood clots run in your family, you may have an inherited clotting disorder, making your blood more likely to thicken abnormally.
- Hormonal Changes – Birth control pills, pregnancy, and hormone replacement therapy can increase estrogen levels, which raises clotting factors in the blood. Pregnant women are particularly at risk due to increased blood volume and pressure on veins.
- Smoking, Obesity & Lifestyle Factors – Smoking damages blood vessels and increases clot risk. Obesity adds pressure on veins, reducing circulation, while dehydration thickens the blood, making it easier for clots to form.
💡 Can You Reduce Your Risk?
Yes! Movement, hydration, and a healthy lifestyle play a huge role in preventing unnecessary blood clots. Small daily changes can make a life-saving difference.
10 Early Warning Symptoms of a Blood Clot
Blood clots rarely announce themselves with a bang; instead, they whisper warning signs that are easy to overlook. But when ignored, these subtle symptoms can turn life-threatening fast. Here’s what to watch for:
1️⃣ Swelling in the Leg or Arm – A sudden, unexplained swelling, especially in one limb, could mean a clot is blocking circulation. If paired with pain, get it checked.
2️⃣ Skin Discoloration – A red, bluish, or pale area on the skin (especially in the legs) could indicate reduced blood flow due to a clot.
3️⃣ Unexplained Warmth in the Affected Area – If part of your leg feels noticeably warmer, a clot may be the cause.
4️⃣ Persistent Cramping in the Calf – If cramps don’t go away with stretching or hydration, a deep vein thrombosis (DVT) could be forming.
5️⃣ Foot or Ankle Pain – Poor circulation from a clot can cause discomfort, aching, or tightness in the foot.
6️⃣ Shortness of Breath – Feeling winded for no reason? A clot in the lungs (PE) may be restricting oxygen flow. Seek immediate medical help!
7️⃣ Sharp Chest Pain – A sudden, stabbing pain in the chest, especially when breathing deeply, could signal a pulmonary embolism (PE).
8️⃣ Unexpected Coughing – Coughing up blood or experiencing a dry, persistent cough could indicate a clot has reached the lungs.
9️⃣ Dizziness & Rapid Heartbeat – If you feel lightheaded, dizzy, or your heart is racing, it could be your body reacting to reduced oxygen from a clot.
🔟 Unexplained Fatigue & Weakness – When your body fights a clot, it works harder, often leaving you feeling exhausted for no clear reason.
💡 Pay Attention to the Signs
Some blood clots are silent. Others send warning signs before things get dangerous. If you notice one or more of these symptoms, don’t wait—get medical help ASAP!
How to Recognize a Medical Emergency
Some blood clot symptoms are mild, but others signal a life-threatening emergency. The key? Knowing when to act fast.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Recognizing a medical emergency can be the difference between early intervention and life-threatening complications. One of the most critical signs to watch for is severe shortness of breath, a sudden inability to breathe properly that may feel like your lungs aren’t getting enough air. This could indicate a pulmonary embolism (PE), where a clot has traveled to the lungs and is blocking oxygen flow.
Another serious symptom is persistent chest pain that doesn’t subside. Unlike mild discomfort, this pain is often sharp, intense, and worsens with deep breaths. It may feel like pressure or tightness in the chest, signaling a clot-related emergency.
Dizziness, sudden fainting, or confusion can also be warning signs, as they may indicate that oxygen supply to the brain has been compromised. Similarly, a swollen, painful leg that feels warm to the touch could suggest deep vein thrombosis (DVT), which, if untreated, could break loose and cause severe complications.
These symptoms should never be ignored. If any of them occur suddenly, seek emergency medical help immediately.
🚑 What to Do in an Emergency?
- Call 911 immediately if you have breathing issues, chest pain, or feel like you might pass out.
- Don’t try to “walk it off”—movement can cause the clot to travel.
- Stay as still as possible until medical help arrives.
Blood clots can escalate quickly, but early action saves lives. Know the warning signs—because seconds matter.
Prevention & Lifestyle Changes to Lower Your Risk
Blood clots may seem unpredictable, but in many cases, they can be prevented with the right habits and lifestyle choices. While some risk factors, like genetics or medical conditions, can’t be controlled, others are completely within your power.
Simple daily actions—like staying active, eating well, and managing your overall health—can significantly reduce the likelihood of clot formation. Prevention isn’t just about avoiding serious complications; it’s about making small, sustainable changes that protect your well-being for years to come.
Keep Your Circulation Moving
One of the best ways to prevent blood clots is to keep blood flowing smoothly. Sitting for long periods—whether during travel, at work, or due to medical conditions—slows circulation and increases clot risk.
Regular movement helps blood stay thin and fluid, reducing the chance of it pooling in the veins. Even simple activities like stretching, walking, or changing positions can make a big difference.
Simple Daily Habits for Prevention
Making a few mindful changes can help protect you from blood clots before they become a problem.
- 🚶♂️ Move frequently – Stand, stretch, or walk every hour to keep blood circulating.
- 💦 Stay hydrated – Drink water regularly to prevent blood from thickening.
- 🥗 Eat clot-friendly foods – Leafy greens, citrus, and omega-3s support vascular health.
- 🚭 Avoid smoking – Smoking damages blood vessels and increases clot risk.
Prevention starts before symptoms appear—by making small adjustments, you lower your risk and stay healthier, longer.
FAQs
How can I reduce the risk of blood clots during long flights?
Prolonged immobility during long flights can increase the risk of developing blood clots, particularly deep vein thrombosis (DVT). To mitigate this risk:
- Stand up and walk down the aisle periodically.
- Flex and extend your ankles to promote blood flow.
- Drink ample water and avoid alcohol or caffeine.
- These can help maintain proper blood circulation in the legs.
Implementing these measures can significantly lower your risk of flight-related blood clots.
Are pregnant women at a higher risk for blood clots?
Yes, pregnancy increases the risk of blood clots due to hormonal changes and reduced blood flow from the legs back to the heart. This risk persists up to six weeks postpartum. It’s crucial for pregnant women to be aware of this elevated risk and consult with healthcare providers for personalized preventive strategies.
How does smoking influence blood clot formation?
Smoking damages blood vessels and alters blood properties, making it more prone to clotting. This elevates the risk of developing conditions like deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE). Quitting smoking is a significant step toward reducing blood clot risks and improving overall cardiovascular health.
Can dehydration lead to blood clots?
Yes, dehydration can thicken the blood, increasing the likelihood of clot formation. Ensuring adequate fluid intake is essential, especially during situations that may promote dehydration, such as long flights, hot weather, or intense physical activity. Maintaining proper hydration supports optimal blood viscosity and circulation.
Blood Flow, Not Blood Woes: Final Takeaway
Blood clots don’t come with a warning siren—but your body does drop hints. The key? Listening before it’s too late.
Swelling? Unusual pain? Shortness of breath? Don’t brush it off. These could be warning signs that your body is displaying for a specific purpose.
The best defense? Know the signs. Stay active. Take action. Blood clots are preventable—and when caught early, treatable.
Your health isn’t a gamble. It’s your power.
So, stay ahead. Stay smart. And most importantly—stay clot-free! 💙