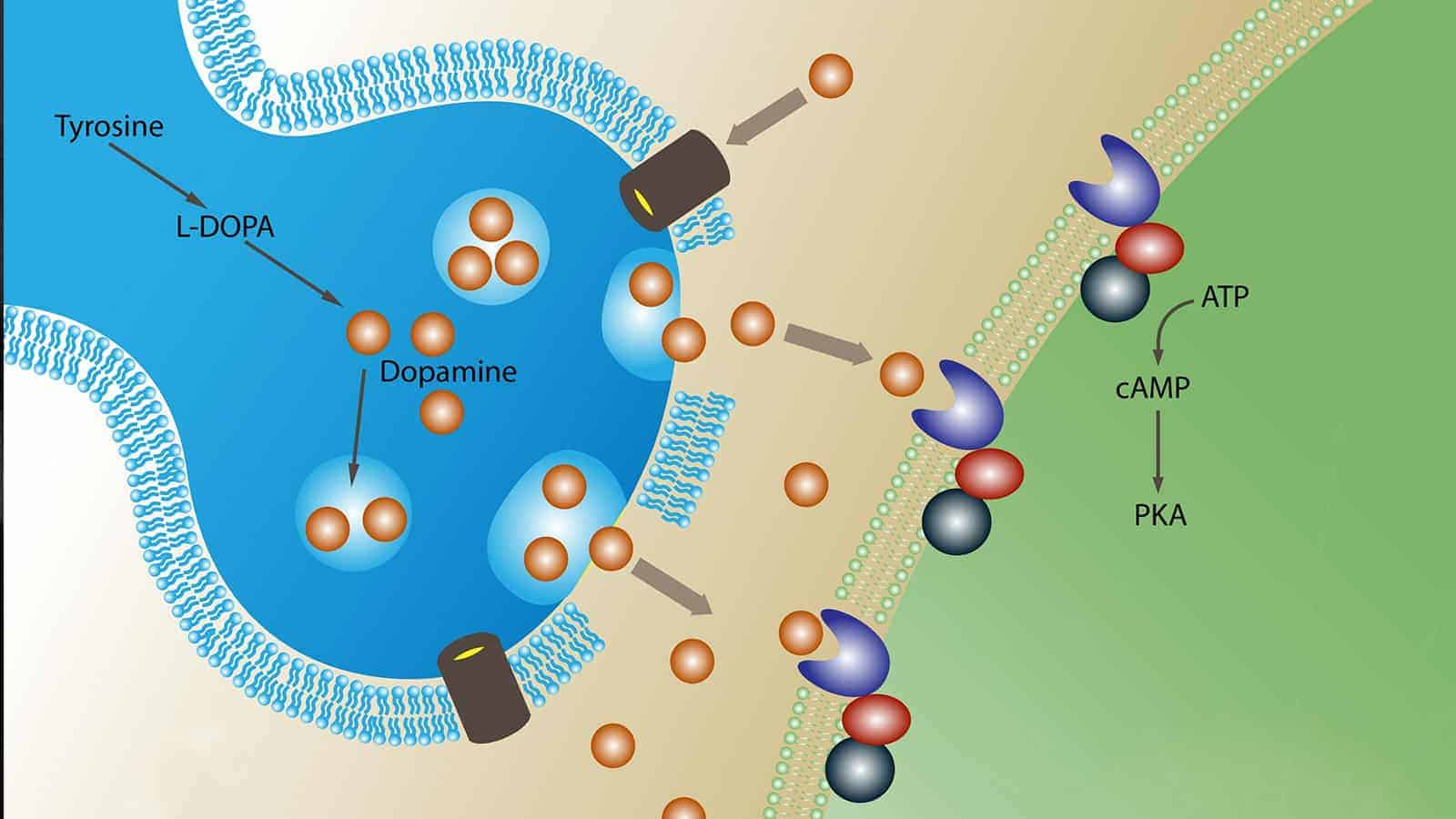
A new study by researchers from the German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD) shows how insulin affects dopamine production. Considered the most important neurotransmitter for the brain’s reward system, dopamine is the “feel-good” hormone. Your brain releases it when you’re anticipating a reward.
When you associate an activity, food, or person with happiness, this raises your dopamine levels. Even thinking about something you enjoy, or smelling your favorite food cooking, could trigger dopamine release. Upon experiencing pleasure from an activity, your brain releases large amounts of dopamine. This action reinforces the craving, and you become focused on fulfilling it more often.
Dopamine can make you feel temporarily euphoric, but it also has a dark side. If you indulge in substances like alcohol, drugs, or certain foods excessively, it can become habit-forming. Eventually, your brain will require ever-higher dopamine production to reach the same pleasure level. You find it harder to resist the temptation, and if you’re not careful, it can lead to full-blown addiction.
Of course, dopamine by itself doesn’t create addiction. Factors such as environmental conditions, genetics, and mental illness also play a role.
Normal dopamine levels contribute to a happy, even mood. The chemical makes you feel alert, motivated, and focused as well.
While making you feel pleasurable is dopamine’s most well-known function, it also plays other important roles. It aids with motor function, decision-making, and even digestion, to name a few.
The Important Role of Dopamine Production

Dopamine production also helps with other bodily functions, including the following:
- blood flow
- executive functioning
- heart and kidney function
- memory and focus
- mood and emotions
- motor control
- pain processing
- pancreatic function and insulin regulation
- sleep
- cortisol regulation
In this study, scientists also discovered how insulin secretion impacts dopamine production. The researchers from DZD in Tübingen found that insulin reduces dopamine levels in a specific brain region called the striatum.
Scientists Reveal How Insulin Impacts Dopamine Production
The striatum resides in the cerebrum and forms part of the basal ganglia. It connects several neural pathways and control circuits in a central location. It’s partially responsible for feelings of motivation, reward, movement, emotion, and other brain functions. According to scientists, this interaction between various functions may influence the brain’s regulation of glucose metabolism and eating habits.
The findings have been published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Globally, rates of obesity and type 2 diabetes continue to skyrocket. In 2016, 13% of the world’s population over age 18 suffered from obesity, and 39% were overweight. Since 1975, worldwide obesity rates have nearly tripled, according to data from the WHO. The organization also stated that about 422 million people globally have diabetes, the majority living in low- and middle-income countries.
Prior studies have shown that the brain plays a crucial role in developing these diseases. Scientists have uncovered how dopamine, the most important neurotransmitter for the reward system, influences these brain changes.
How Dopamine Production Works
After you eat, your brain releases the hormone insulin, which regulates the metabolism. It’s not yet fully understood how dopamine and insulin interact. However, changes in these systems have been associated with a greater risk of obesity and diabetes. So, researchers from the DZD, in collaboration with the Institute of Diabetes Research and Metabolic Diseases (IDM), wanted to solve this mystery. Tübingen University Hospital (Innere IV, Director: Prof. Andreas Birkenfeld) also participated in the study.
The researchers investigated how these systems influence and interact in the reward system, with a specialized focus on the striatum.
“Our eating behavior is regulated by the interaction between the reward system and homeostatic systems. Studies indicate that insulin also acts in dopamine-driven reward centers in the brain. It has also been shown that obesity leads to changes in the signaling of the brain that have a negative effect on the glucose metabolism in the whole body,” said first author Stephanie Kullmann. “We now wanted to decipher the interaction between the two systems in humans and find out how insulin regulates the dopamine system.”
The Study on How Insulin Impacts Dopamine Levels
For the research, ten healthy, normal-weight men received insulin or a placebo via a nasal spray (randomized, placebo-controlled, blinded crossover study). When a person absorbs insulin through the nose, it reaches the brain immediately.
To analyze how insulin interacts with dopamine, the scientists utilized an innovative measurement method. They combined magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to assess brain activity and positron emission tomography to measure dopamine production.
Their analysis revealed that administering insulin via the nasal cavity reduced dopamine levels. It also caused changes in the brain’s network structure.
What the Experts Say:
“The study provides direct evidence of how and where in the brain signals triggered after eating — such as insulin release and the reward system — interact,” said Professor Martin Heni, last author of the study. “We were able to show that insulin is able to decrease dopamine levels in the striatum in normal-weight individuals. The insulin-dependent change in dopamine levels was also associated with functional connectivity changes in whole-brain networks. Changes in this system may be an important driver of obesity and related diseases.”
The team wants to study changes in dopamine production and insulin levels in obese and diabetic volunteers in future studies. This population suffers disproportionately from insulin resistance when the body can’t absorb glucose properly. This condition leads to high blood sugar, which may eventually result in diabetes.
The researchers believe this resistance inhibits insulin from regulating dopamine production in the brain’s reward system. So, in further research, they hope to uncover a behavioral or medicinal treatment to balance insulin levels in this population.

Final Thoughts on How Insulin and Dopamine Interact in the Brain
Most people associate dopamine with the euphoric high you get after exercising or eating a chocolate chip cookie, for instance. However, scientists from the German Center for Diabetes Research have found that high insulin levels can inhibit the feel-good hormone. They believe that these changes in the brain may play a significant role in causing diabetes and obesity. In the future, they hope to discover more about possible treatments that may help restore insulin to healthy levels.