What is UTI?
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is defined as “an infection in any part of your urinary system – your kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.” The majority of UTIs occur in the bladder and urethra.
Being a female can be considered a risk factor for UTI. Women are as much as 30 times more likely to develop this infection than men. There are a couple of reasons for this. First, women have shorter urethras than men, meaning that bacteria have a better chance of infiltrating the bladder. Additionally, the female urethra is closer to the rectum, increasing the risk of germs spreading from the latter.
UTI complications can be severe. Unless the infection is treated promptly, complications may include:
- Sepsis, a life-threatening blood infection where the immune system is compromised.
- Recurring infections
- (For pregnant women) premature birth or low birth weight
- Long-term kidney damage or acute kidney infection
- (In men) narrowing of the urethra (gonococcal urethritis)
Risk factors for UTI
Additional risk factors associated with UTI include:
- Kidney stones or enlarged prostate
- Abnormal urinary tract physiology
- A suppressed immune system
- Use of a catheter
- Urinary surgery procedure
- Previous UTIs (around 40 percent of people who have one UTI will have a second.)
Signs of UTI to Never Ignore
If you experience any of the following symptoms, please seek medical care. (Also, continue reading after this section for prevention tips!)
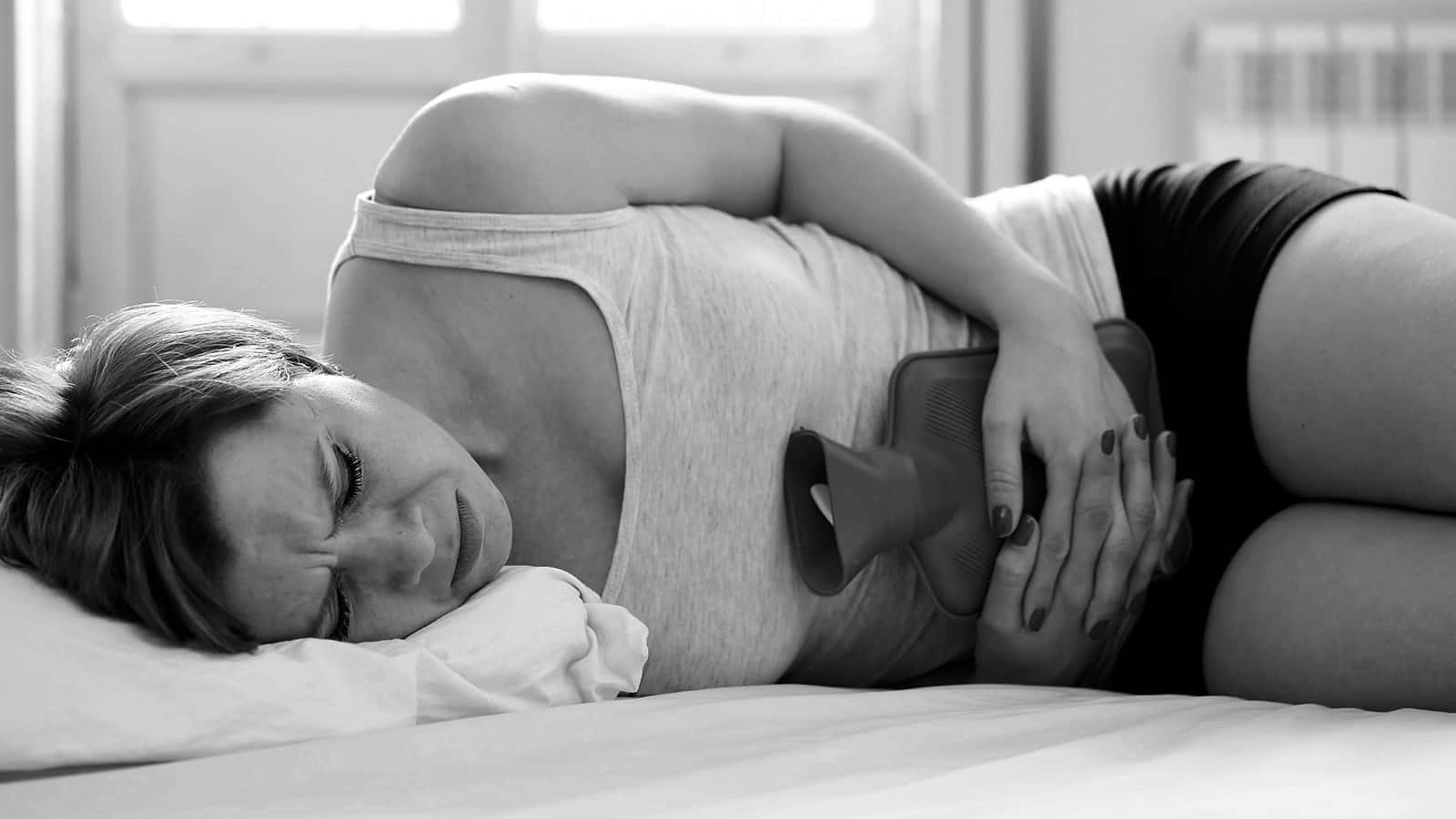
Abdominal Pain
When bacteria are transferred from the rectum to the urethra, and up to the bladder, abdominal pain can result. Overgrowth of E. Coli, a common bacteria found in UTIs, may worsen due to a slow immune system response – and may trigger painful symptoms.
Aching and cramping of the lower abdomen are among the most common symptoms of UTI. When this pain is frequent and ongoing, it is wise to seek the advice of a medical professional.
Exhaustion
For some reason, the immune system can be a bit slow in responding to a urinary infection. If this happens, when the immune system does get to work, it will kick into overdrive. An immune system in overdrive requires a considerable expenditure of energy – and this can quickly drain us.
The only antidote here is to get plenty of rest following proper treatment.
Frequent Urination
The presence of an infection in the urinary tract can play games with your bladder. No doubt you’ve felt the urge to go pee only to find that you don’t have much “in there.” This false sense of urgency is a common symptom of UTI.
Speaking of pee, you may also find that yours may smell a bit funny. The presence of bacteria in the urine may produce this strange smell.
Urine discoloration
Normally-colored urine is light yellow to yellowish-brown, depending on your hydration levels. (It should almost always be the former color, by the way!) But urine that appears cloudy, gray, or pink may indicate the presence of bacteria. Blood in the urine is a possible sign also, and one that requires medical intervention.
(Foods such as beets, blackberries, and rhubarb may also alter urine color.)
Pain while urinating
The development of white blood cells, or pyuria, causes inflammation of the bladder wall. This inflammation, combined with the infected urine, is what produces pain and irritation during urination.
It’s also likely that your pee will produce a pungent odor. This is also a byproduct of bacteria within the urine.
Stomach flu-like symptoms
Besides abdominal pain, you may experience symptoms that resemble a stomach bug. If the infection spreads to the kidneys – which is a result of delayed treatment – symptoms become more severe and variable. These symptoms include a backache, chills, fever, nausea, and vomiting.
If you are also experiencing pelvic discomfort and or pain while urinating, it is wise to see a doctor, as your infection may have possibly spread to the kidneys.
Prevention and Treatment of UTI
As prevention is always the best medicine, we like to start here. To prevent UTI, here are some tips:
- First, drink plenty of water.
- Try some cranberry juice.
- Also, avoid feminine products with fragrances.
- Urinate after intercourse, if necessary.
- Finally, choose a new method of birth control (talk to your doctor or wellness professional about this one).
Treatment of UTI usually comes in the form of prescription antibiotics. Typically, antibiotics will clear up the condition within a few days. For more severe infections, a longer treatment duration and or a stronger type of antibiotics may be prescribed. Additionally, your doctor may prescribe a pain medication to relieve the irritation and burning during urination.
Other potential treatments include:
- Intravenous (IV) antibiotics
- Self-treatment (on doctor’s approval)
- Estrogen therapy
- Alternative remedies, including probiotics, garlic, and apple cider vinegar (there are plenty of natural remedies that may reduce UTI symptoms.)
https://youtu.be/dDn84WupgBA