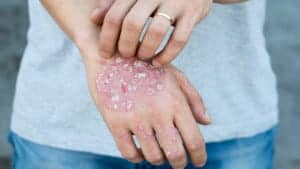
Atopic dermatitis, more commonly called eczema, is a chronic condition that causes the skin to become itchy and red. It is most commonly starts in childhood but can begin at any age. In addition, asthma or hay fever may co-exist.
More than 30 million people suffer from eczema in the United States. Although the cause of dermatitis is unknown, researchers know that genetic and environmental triggers usually prompt its development.
Atopic dermatitis typically affects the hands, face, scalp, backs of the knees, and the inside of the elbows. However, it can affect any part of the body.
It is generally itchy. But, for some, the itch is mild. While for others, the itch is severe. In fact, it often causes the skin to become extremely inflamed. For some of these patients, the itch is so severe that they scratch until the skin bleeds.
Symptoms of Eczema
- Severe itching
- Oozing or crusting
- Patchy areas of swelling
- Red, inflamed skin
- Patches of rough, scaly or leathery skin
- Dark, patchy colored skin
- Dry, sensitive skin
Complications include:
- Skin infections
- Sleep problems
- Chronic itchy, scaly skin
- Irritant hand dermatitis
- Asthma and hay fever
- Allergic contact dermatitis
Flare-up Prevention for Eczema Patients
Preventative measures help eliminate flareups and mitigate the negative drying effects of bathing. Recommendations include:
Regularly moisturizing the skin twice a day
- Regularly moisturizing the skin twice a day – Lotions, ointments, and creams help the skin retain moisture by sealing it in.
Identifying and avoiding triggers
- Identifying and avoiding triggers – Triggers include dust, pollen, stress, soaps, obesity, sweat, and detergents.
Drying the skin carefully
- Dry the skin carefully. Use a soft towel to pat-dry the skin and ensure to moisturize the skin while it is damp.
Unfortunately, there is no current cure for atopic dermatitis. However, natural remedies and efficient self-care can help relieve symptoms and prevent flareups.
Natural Remedies for Eczema
Note: Symptoms of dermatitis may mimic those of other conditions. It is important to get an eczema diagnosis confirmed by a health care provider before starting any form of treatment.
Depending on the severity of the condition, a physician may prescribe medications to help alleviate symptoms. There are also many natural remedies available that can help provide symptom relief.
Here are 15 effective natural remedies for treating eczema.
Aloe Vera Gel
Aloe Vera gel is a rich source of medicinal properties for human health. Research on the benefits of Aloe Vera are primarily focused on the biological properties of the Aloe species, most notably being its antibacterial and antimicrobial capabilities.
Along with the antibacterial and antimicrobial properties of Aloe Vera gel, researchers have reported that the plant also boosts the immune system and promotes wound healing. These properties help prevent infections and soothe inflamed skin.
Colloidal Oatmeal
Avena sativa, or colloidal oatmeal, is a natural supplement with many skin-healing capabilities. In fact, its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant functions improve:
- Skin roughness
- Scaly skin
- Dry skin
- Itchiness
Colloidal oatmeal is made from boiled ground oats. Then, the process extracts the oats’ healing nutrients. It is generally safe for people of all ages. However, individuals allergic to oats should avoid products containing colloidal oatmeal.
Coconut Oil
Coconut oil is known for its many health benefits, as it helps reduce inflammation. Specifically, coconut oil contains lauric acid, which is used to create monolaurin. Monolaurin is an antimicrobial agent capable of fighting pathogens, including fungi, viruses, bacteria, and yeast.
In particular, coconut oil:
- Hydrates the skin
- Minimizes the presence of pathogens
- Diminishes pain and inflammation
- Decreases oxidative stress
Tea Tree Oil
Tea tree oil is extracted from the Melaleuca alternifolia tree. This essential oil is often used to alleviate symptoms related to skin problems, including dermatitis.
Tea tree oil contains several compounds that have been shown to eliminate certain types of viruses, bacteria, and fungi. These compounds make tea tree oil an effective natural remedy for preventing infections, promoting wound-healing, and treating skin disorders.
Sunflower Oil
Sunflower oil is an extract taken from sunflower seeds. It protects the outer layer of skin by retaining moisture and eliminating bacteria. The hydrating properties of sunflower oil may help reduce inflammation and itching.
Evening Primrose Oil
Evening primrose oil – an extract from the evening primrose plant – contains gamma-linolenic acid and omega-6 fatty acids. When applied topically, evening primrose oil – calms irritated skin. When ingested orally, it may help prevent systemic inflammation.
Calendula Oil
Calendula oil is an extract from the marigold flowers of the Calendula officinalis plant. Because it has antibacterial, antifungal, and anti-inflammatory capabilities, it can help to:
- Heal wounds
- Soothe inflamed skin
- Reduce rashes.
Witch Hazel
Humankind has used witch hazel topically as a remedy for skin irritation and inflammation for centuries. It is often used to calm inflamed skin, minimize itching, and dry any leaking.
Witch hazel contains antioxidants that can minimize inflammation. That is because of pro-anthocyanins, a component of witch hazel that helps the skin by improving water retention, minimizing redness, and controlling the irritative process.
Research also indicates that witch hazel may help control the growth of bacteria. This is especially important, as dermatitis may cause bacterial overgrowth on the skin.
Apple Cider Vinegar
Apple cider vinegar is one of the most popular natural health remedies.
Items with a pH below 7.0 are acidic, and those above 7.0 are alkaline. The natural pH of healthy skin is under 5.0. However, the pH levels of the skin for individuals suffering from atopic dermatitis are generally higher.
High acidity levels promote the breakdown of the skin’s protective microbiota. And, apple cider vinegar is a mild acid. Therefore, it may help return the skin to its natural pH level.
Honey
Honey’s nutritional components are traditionally known for their medical capabilities. Honey has not only natural anti-inflammatory properties but also antibacterial properties. Honey also boosts the immune system and helps treat wounds and burns.
In a 2003 study, a honey ointment mixture containing honey, beeswax, and olive oil showed a substantial reduction in dermatitis-related itchiness in 80 percent of users.
Probiotics
Probiotics help balance “good” and “bad” bacteria in the digestive system. These good bacteria are thought to strengthen the immune system by increasing the number of “good” bacteria in the gut.
A stronger immune system helps combat the inflammation that causes dermatitis.
Diet
Eczema is triggered by several factors, including allergens, stress, and food.
Some foods can induce or reduce inflammation, so simple dietary changes can help prevent flares.
Foods that combat inflammation include:
- Fruits and vegetables
- Beans and lentils
- Turmeric and cinnamon
- Fish
- Leafy greens
Foods that may induce inflammation include wheat, eggs, dairy, and soy. Thus, avoiding these foods may help identify the causes of flares.
Acupuncture and Acupressure
Acupuncture is a form of Traditional Chinese medicine. In this practice, fine needles are inserted into specific points of the body to change energy flow.
Acupressure is a different form of Traditional Chinese medicine. In it, therapists use their hands to apply pressure on parts of the body.
Both practices may help relieve itchiness.
Cool Baths
Regular baths are important for treating atopic dermatitis.
Dry skin occurs when the skin can’t properly retain water. However, washing too much or using harsh soaps often dries out the skin, which further aggravates the condition.
The “Soak and Seal” is a method for treating dermatitis. Doctors recommend taking a cool bath – using a gentle cleanser – for five to 10 minutes. Furthermore, avoid using hot water, as it dries out the skin.
Then pat-dry and use caution to keep the skin damp. Finally, generously apply a moisturizer within three minutes to prevent the air from drying the skin out. This method helps the skin seal in moisture.
Therefore, the National Eczema Association recommends that adults with eczema should:
- Take shorter baths or showers
- Use warm, rather than hot, water
- Bathe or shower once a day
- Use gentle cleansers
- Moisturize after washing up
- Humidifiers
So…Dry air causes dry skin.
Dry air is especially problematic in cold-weather months, during which the heat from heaters removes moisture away from the skin.
Thus, using a humidifier helps the skin retain moisture, keeping skin hydrated and preventing inflammation and irritation.
Final Thoughts on Coping with Eczema
Although there is no cure for eczema, you can rely on natural remedies to help ease symptoms.
Natural remedies include gels, oils, baths, and dietary changes that help reduce inflammation, combat infection, and moisturize the skin.
Remember, you should get a diagnosis from your family doctor or a dermatologist before beginning treatment. Furthermore, a health care practitioner may prescribe medications to help treat inflammation in severe eczema.