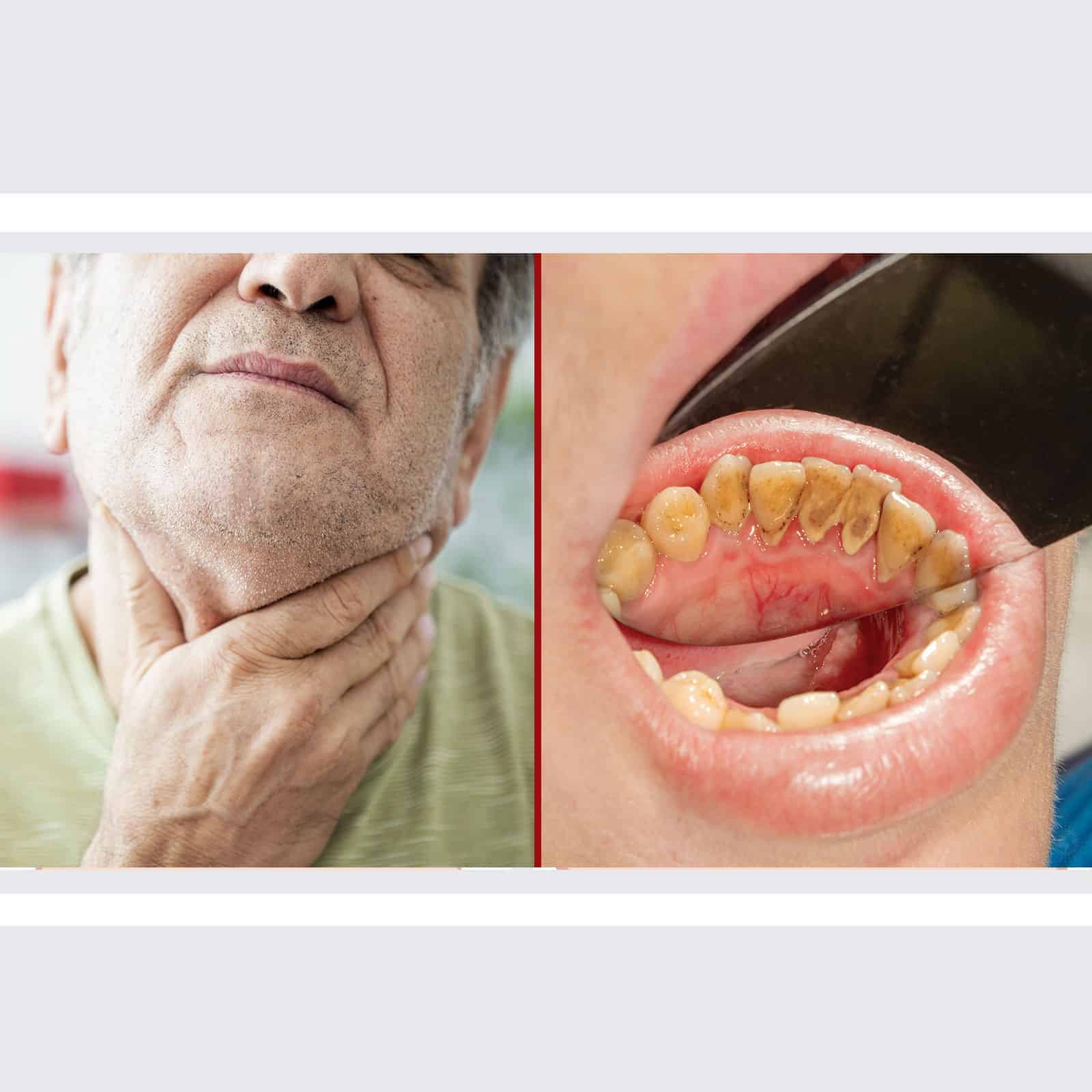
Oral cancer affects more than 35,000 people each year in the United States. Though it’s not often talked about, it’s just as common as leukemia. Primarily, mouth cancer affects men over 60 years of age, but some women get it too.
Mouth cancer is anything that affects the oral cavity, which includes the tongue, lips, cheek, palate, uvula, gums, or the salivary glands. However, it’s a generic term that refers to any malignancy within the mouth, neck, thyroid, and certain parts of the head. It’s even possible to have tonsil and jaw cancer, though that is extremely rare.
Signs and Symptoms of Oral Cancer
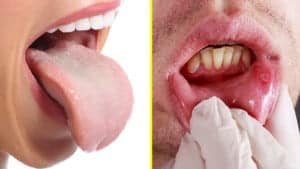
Many people get sores inside their mouth for random reasons, and usually, there is no fear that it’s cancerous. Jaw cancer, or any other malignancy in the oral cavity, begins when the healthy cells in the mouth break down abnormally.
The changes can be gradual, or they can happen quickly. The most common sign is red or white patches, which are ulcerations that won’t heal. The white spots tend to be the most common, and their proper medical term is leukoplakia. While the white patches aren’t always malignant, they can quickly become cancerous.
The red patches are called erythroplakia, and they are almost always malignant. When a person has a presence of both white and red spots, then the medical term erythroleukoplakia is used. Other than the irregular patches, here are some other signs of concern.
Primary signs of oral cancer:
•Bleeding in the oral cavity
•Losing teeth or loose teeth
•Pain when swallowing
•Problems when wearing dentures because of sores
•Lump(s) in the neck area
•Earaches
•Altered facial appearance
•Pain in the mouth, neck, or head
•Weakness
•Dry mouth
•Frequent infections of the throat, or gums
•Thyroid issues
•Hair loss
•Nausea and vomiting
•Diarrhea
•Changes in your voice
Cancer forms during the process of making new cells. As the cells become old or damaged, they will perish so that new cells can replace them. In some people, the process becomes interrupted as something goes wrong. When cells don’t die off like they should, then the new cells build on top of them, forming masses.
While these masses are not always malignant, these tumors must be evaluated. If there is cancer in the mass, the troubled cells will slowly break away and enter the blood or lymphatic system. Since these vessels branch out into the entire body, the malignancy will spread.
Most commonly, mouth cancer spreads to the neck first as it’s the closest area. Any signs of mouth or tongue cancer need to be evaluated quickly. When dealing with a tumor, time is of the essence. The earlier it’s caught, the better the long-term prognosis.
Causes of Mouth and Tongue Cancer
When it comes to the mouth or oral cancer, the leading causes in the United States are alcohol and tobacco. The chemicals found in these products cause damage to the cell’s DNA, which can lead to cancer formation. Both alcohol and tobacco are considered dangerous because of their chemical content.
Many things can increase your risk of developing mouth cancer, which includes smoking and drinking alcohol together. Medical experts are not sure what triggers the cellular DNA abnormalities that turn into a malignancy. Additionally, there are more than 41 million people alone who smoke cigarettes, so the number of individuals that get oral cancer is relatively small in comparison.
Risk Factors To Examine
Some risk factors for developing mouth cancer include having an unhealthy diet, eating betel nuts, using smokeless or chewing tobacco products, having HPV or human papillomavirus, and having poor oral hygiene.
•Smokeless Tobacco
Products that fall under the smokeless tobacco category include snuff and chewing tobacco. Not only does using these products increase your chances of developing mouth cancer, but you may also have issues with pancreatic, stomach, liver, or esophageal cancers.
The carcinogenic juices escape during the “chewing” process and travel to other areas of the body. While some see these products as a safer alternative to smoking, they are just as dangerous, if not more.
•Oral Hygiene
Your dentist always told you the importance of brushing and flossing your teeth. This process removes toxins that can decay inside your mouth. Cancer l to the development of wounds in your oral cavity.
These wounds can be caused by broken teeth that have jagged edges that make cuts on the tongue or gums. Additionally, poor oral health can cause ulcers or wounds to form on the gums, tongue, or roof of the mouth once these sores are in the mouth, the chance of oral cancer increases.
When you consider that your oral hygiene can make a significant impact on the possibility of developing cancer, brushing your teeth seems more critical.
•Your Diet
Medical research reveals that your unhealthy eating habits can have a direct link to your risk of developing mouth cancer. When you eat a healthy, well-balanced diet, it’s believed that it reduces the risk of having any significant oral issues. The fiber and necessary vitamins inside fruits and vegetables are imperative for your body.
•Human Papilloma Virus(HPV)
HPV was first discovered in the late 1980s, but it’s quickly become a significant concern for those in their late 20s, though it can affect people of any age. HPV is a cluster of viruses that affects the moist membranes within the body. Most commonly, the areas affected are the mouth, throat, cervix, and the anus.
HPV spreads through sexual contact, but all you need is skin-to-skin associations to transfer this dangerous disease. Though it’s rare, there is significant evidence that shows that some of the strains of human papillomavirus can trigger the abnormal growths that cause oral cancer.
•Betel Nuts
Many people won’t recognize the betel nut because they are native to Asian communities. While people from Sri Lanka, Pakistan, and Bangladesh use them often, they are not readily available for purchase in the United States.
The risk of mouth cancer is significantly higher in these areas because people chew on these nuts as it has a stimulant effect. Some compare the taste and feeling of drinking a cup of coffee. Betel nuts have a carcinogenic impact like tobacco, which means they can increase the chances of developing an oral malignancy.
In the United States, some tobacco companies will add a bit of betel nut to their blend because of the enhanced feeling that it gives to their users. The popularity of this seemingly harmless nut is beginning to catch on, though it’s not innocent at all.
Diagnosing Mouth Cancer
If you are having issues that you believe could be mouth cancer, then you need to have some tests run. Many people start at a dentist and switch to a specialist to handle the issue. The medical team will need to know your complete history, including whether you’ve used tobacco or alcohol.
You will be referred to both radiologists and pathologists who specialize in these types of cancers. The first step will be to conduct a biopsy of the questionable area.
•Oral Tissue Biopsy
The first step in determining if you have mouth cancer is to have an oral tissue biopsy. The surgeon will remove a small piece of the abnormal tissue to have it analyzed at a lab. A pathologist will receive the sample and look at it under a microscope so that they can make an official diagnosis.
•Diagnostic Imaging
Once cancer has been identified, your doctor may want to take a series of x-rays. They will look at the lower jaw and sinus area. The goal of the imaging is to see if cancer has spread and how deep it has gone. They can use a CT, MRI, or a special x-ray called a Panorex.
•Genomic Testing
If your cancer is advanced, then the oncologist will want to do tumor sequencing. Also called molecular profiling, it will look at the cells that they obtained from your biopsy to see if any genetic mutations are present. In many cases, they find that a change in your genes is related to the type of cancer in your body.
Gathering genetic information is essential for treatment. Additionally, it can help predict the chances of cancer reoccurring.
Final Thoughts: Treatment Options
Treating mouth cancer is complex, and it depends on a person’s beliefs and preferences. The hallmark treatment is chemotherapy and radiation; however, there are holistic methods that, while controversial, prove just as useful. Some people won’t require treatment as surgical intervention is all that is needed.
Many variables come into play when you’re facing oral cancer, so you need to have a medical team that can work with you to find the best solution. Dealing with cancer is something that no one wants to face. Thankfully, the five-year survival rate is over 69 percent, which means it’s a highly treatable form of malignancy.