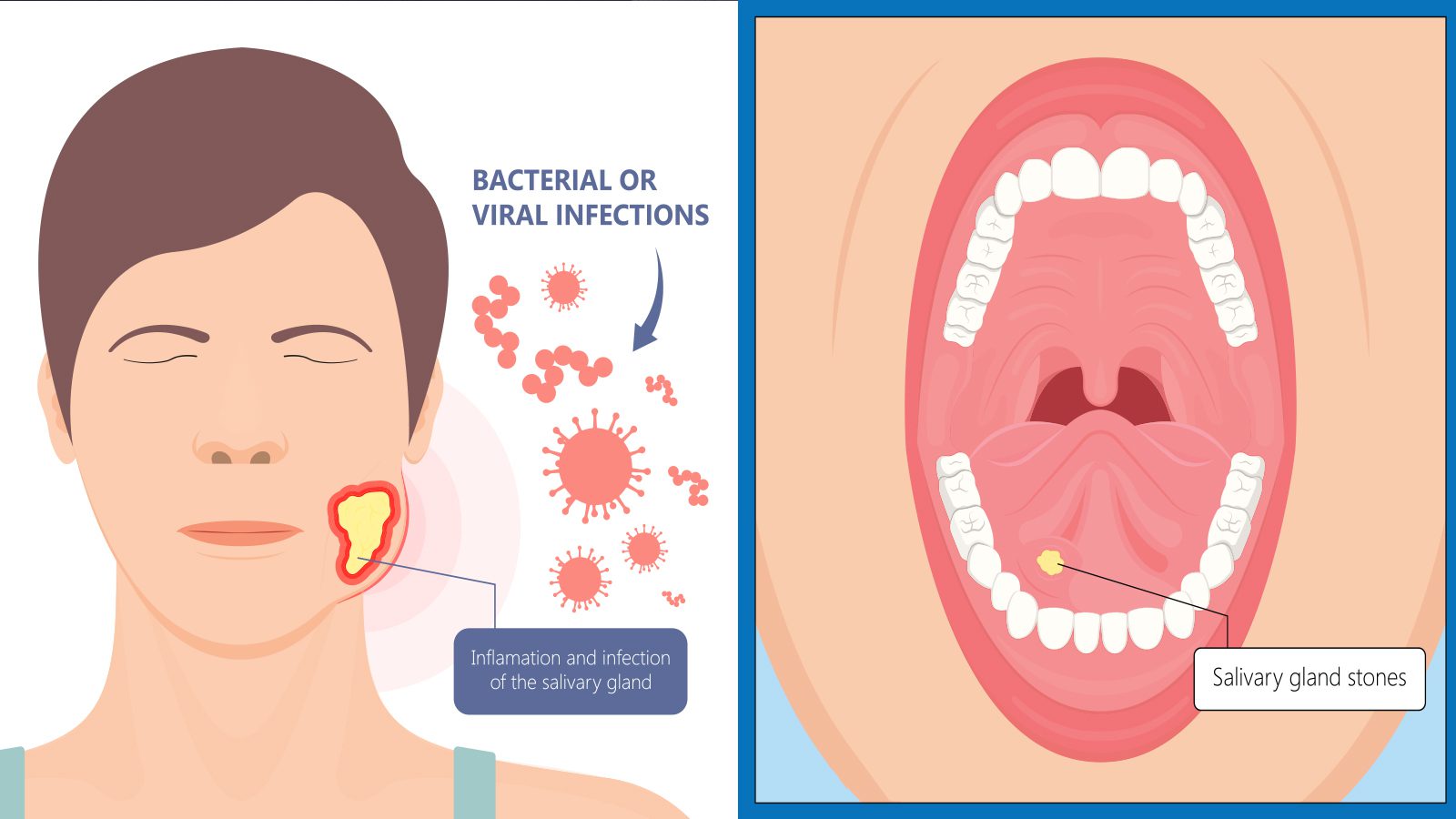
Salivary stones, also called Sialolithiasis, is a condition that causes benign calcified masses in the salivary glands or ducts. These mouth stones can lead to pain, cheeks and tongue inflammation, and saliva obstruction if left unaddressed. Calcium buildup in the salivary ducts occurs due to several factors, including dehydration, certain autoimmune disorders and medications, and poor oral hygiene.
However, avoiding salivary stones is simple, with specific preventative measures such as practicing proper oral hygiene, staying hydrated, and avoiding tobacco and alcohol. Eating a balanced diet can also help prevent mouth stones and enhance oral health. Understanding the factors that lead to the formation of salivary stones can help you prevent them and maintain a healthy mouth and gums.
Symptoms and Signs of Salivary Stones
- Pain and discomfort in the affected salivary gland area. The pain can worsen during eating or when the salivary gland is stimulated.
- Swelling or enlargement of the affected salivary gland.
- Redness or inflammation in the area around the salivary gland.
- Difficulty opening the mouth completely.
- Dry mouth or decreased saliva production.
- Foul taste in the mouth.
- Difficulty or pain while swallowing.
- A visible or palpable lump or hard mass in the salivary gland area.
- Pus or discharge from the duct opening if there is an associated infection.
- Recurrent or persistent episodes of swelling or pain in the salivary gland area.
It’s important to note that not all individuals with salivary stones will experience all of these symptoms. The specific symptoms can vary depending on factors. These include the size and location of the stone, the presence of infection, and individual variations in pain threshold. If you suspect you have salivary stones or see symptoms related to your salivary glands, consult your doctor or dentist for proper evaluation and management.
How Large Are Salivary Stones?
The size of salivary stones can vary greatly. They can range from tiny grains to larger formations that block the ducts completely. Treatment options for salivary stones may include conservative measures like hydration, warm compresses, and stimulation of saliva flow. If you ignore it, doctors may prescribe invasive procedures like stone removal or surgical intervention. It all depends on the size and location of the stone.
Seven Primary Causes of Salivary Stones (Mouth Stones)
Below, we’ll discuss seven significant causes of calcium buildup and how to keep stones from forming.
1 – Dehydration Can Lead to Salivary Stones
One of the primary triggers for the development of salivary stones is dehydration since inadequate water intake thickens the saliva. When this happens, it becomes more concentrated, increasing the risk of calcium buildup. You may experience swelling if the stones block your salivary ducts, which causes saliva to accumulate in the glands. However, maintaining proper fluid balance can reduce your risk of developing these painful mouth stones. Doctors recommend drinking at least a liter and a half daily to hydrate your body. Additionally, you should drink more if you live in a hot environment or exercise intensely.
2 – Poor Oral Hygiene
Improper oral hygiene may also lead to calcium and bacteria buildup in the mouth, increasing your risk of developing salivary stones. Dentists recommend flossing, brushing your teeth at least twice daily, and scheduling regular cleanings to eliminate plaque. Taking care of your oral health will lower your chances of developing an infection due to harmful bacteria.
3 – High Calcium Intake
Poor eating habits may also lead to the formation of mouth stones since certain foods can disrupt the mineral balance in your body. For instance, consuming too much calcium can cause it to crystallize in the salivary ducts and form stones. Also, studies show that a magnesium and citrate deficiency may cause mouth stones to develop.
To prevent calcium buildup in the salivary glands, follow a balanced, nutritious diet and avoid consuming excess calcium. Also, watch your intake of processed, sugary foods since these can result in harmful bacteria growth in the mouth and gut.
4 – Certain Medications
Certain medications, such as blood pressure drugs, antihistamines, and diuretics, may also result in salivary stones because they reduce saliva flow in the glands. If you take any of these medicines, discussing side effects and drug interactions with a healthcare professional to prevent calcium buildup is essential.

5 – Tobacco and Alcohol Use
Also, certain lifestyle habits such as tobacco and alcohol consumption may trigger mouth stone formation. Studies show that excessive intake of cigarettes and alcohol can cause oral cavity inflammation due to harmful bacteria. Research also shows that long-term smoking can reduce salivary flow and antimicrobial proteins, which help maintain optimal oral health.
It’s best to avoid tobacco and limit alcohol consumption to prevent salivary stones. If you have trouble quitting smoking, you can try nicotine replacement therapies, practice mindfulness or meditation, or speak with a counselor who can help you overcome the compulsion to smoke. When it comes to alcohol, drinking it occasionally or even moderately probably won’t cause harm. However, limit your consumption to one to two drinks per day for the best health outcomes.
6 – Obstruction or Infection in Salivary Glands
A salivary gland obstruction or infection can also cause salivary stones to form. If you have a bacterial staph infection or excess calcium in the body, your salivary glands can swell, which blocks saliva flow. When this happens, harmful bacteria will accumulate and cause pain, swelling, or even fever in some cases. If you have mouth stones, you may also experience facial and neck tenderness, difficulty swallowing, and a dry mouth.
If you suspect you have mouth stones, make an appointment with your doctor immediately so they can treat them before they cause further damage. Sometimes, they may recommend home remedies such as sucking on lemon drops, drinking plenty of water, or using heating pads to dislodge the stones. In other cases, your doctor may force the stone out by massaging on both sides of the duct or use extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) to break the stone into smaller pieces.
7 – Autoimmune Disorders
Certain autoimmune disorders, such as Sjogren’s syndrome and lupus, can trigger the formation of salivary stones. These diseases reduce salivary flow and trigger inflammation of the salivary glands, making it more likely for mouth stones to form. While there isn’t a cure for these disorders, you can still manage them by utilizing proper oral hygiene, drinking plenty of water, and using warm compresses on the glands to reduce swelling.
Four Tips for Preventing Salivary Stones
The following tips can help in the prevention of salivary stones:
- Drink plenty of water. As we said above, drink at least two to three liters daily for adequate hydration.
- Practice good oral hygiene. Brush and floss your teeth twice daily. Next, use a mouthwash that eliminates excess plaque and tartar buildup and promotes oral health.
- Eat a balanced diet. Practicing positive lifestyle changes like limiting calcium and consuming plenty of fresh foods such as fruits and vegetables can help prevent salivary stones. Also, limit your intake of processed, sugary foods that cause unhealthy bacteria to thrive.
- Schedule regular dental check-ups and discuss any problems with healthcare professionals.
Final Thoughts on Maintaining Oral Health for Salivary Stone Prevention
Salivary stones form due to poor oral hygiene, dehydration, certain autoimmune disorders and medications, and tobacco and alcohol consumption. High calcium intake and infections of the salivary glands may also contribute to salivary stones. However, you can help prevent these painful mouth stones by prioritizing positive oral hygiene, drinking plenty of water, and eating a balanced diet.