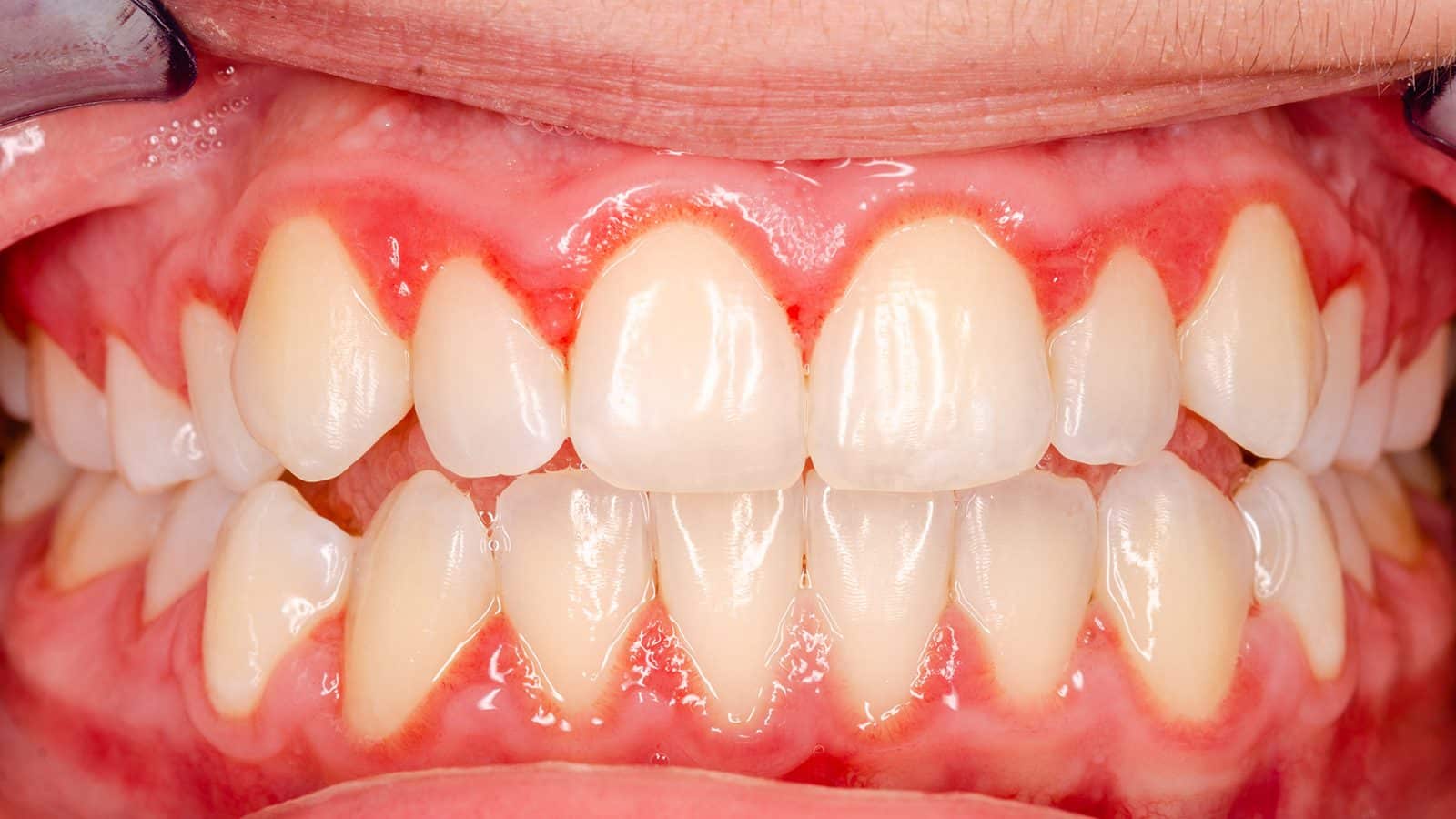
Gum health is a good indicator of overall well-being.
Dental professionals provide insights into the possible causes and underlying health conditions associated with swollen gums.
Swollen gums aren’t something you should ignore because it could indicate other issues. They can swell for many reasons, from gum disease to infections and hormonal changes. Determining the problem allows you to get treatment and live a healthier life.
Understanding swollen gums and the potential health implications can encourage you to seek help. You can discuss it with a profession to determine how to reverse the effects and prevent them from swelling again.
Understanding Swollen Gums
Swollen gums can be a temporary or permanent oral health issue, depending on the cause. Its cause is often not brushing effectively because bacterial plaque accumulates on your teeth. However, many other complications can lead to swelling.
Oral health issues can contribute to other complications, so don’t ignore swelling. It can also make you feel embarrassed when the inflammation is visible, leading to hiding your smile or holding back laughter. Poor oral health can even lead to social isolation if it depletes self-esteem and confidence enough.
Additionally, you could experience pain while eating or drinking and discomfort that leads to difficulty concentrating. The underlying cause of gum inflammation can also worsen or cause further issues.
Gum swelling symptoms involve discoloration of your gums, including red or purple, from blood flow increase. Other signs include a smooth or shiny appearance and bleeding. You might also experience irritation or sensitivity.
7 Things Swollen Gums May Indicate About Your Well-being

1. Oral Hygiene Issues
Poor oral hygiene can cause swelling due to plaque buildup and tartar on your teeth. When you have plaque, it means there’s a film of bacteria and food particles on your teeth. After a few days, plaque hardens into tartar that can’t get cleaned off with brushing or flossing.
An abscessed tooth, or infection, is another result of oral hygiene issues that can lead to swelling. This issue typically causes swelling around one tooth, but it can spread if you don’t get treatment.
Other times, swelling could happen if you have a food particle stuck in your gums. If this is the case, you’ll likely get relief from removing the food by brushing and flossing.
Practicing good oral hygiene makes a difference, so make sure to:
- brush your teeth at least twice daily
- floss once daily
- get regular dental checkups and treatment
- use sugar-free toothpaste that contains fluoride
- stay hydrated to stimulate saliva production
2. Gum Disease
All stages of gum disease, or periodontal disease, can cause swelling. This disease damages the soft tissue around your teeth and can lead to complications. The stages include:
- gingivitis (early-stage)
- periodontitis (advanced)
- trench mouth (severe)
The symptoms of gingivitis are often mild, and you might not notice them right away. These symptoms involve irritation, redness, and swelling on the gum around the base of your teeth. You may also notice bleeding gums, hot or cold sensitivity, and bad breath.
Gingivitis can occur from tartar buildup, so it’s essential to get regular dental cleanings. A dentist can remove the tartar to prevent further issues.
This condition is common but leads to periodontitis if you don’t get treatment quickly. Once it advances, it results in more intense symptoms and sometimes causes you to lose teeth.
When periodontitis sets in, you could experience receding gums, bad breath, and painful chewing. Studies show it can also contribute to the development of cardiovascular disease and other complications. Smoking cigarettes, poor oral hygiene, stress, diabetes, and genetics can make you more likely to develop this condition.
After that stage, trench mouth could occur, causing painful ulcerations on your gums as bacteria build up. The symptoms also involve gray-colored gums, a foul taste, and sometimes fever or fatigue. Trench mouth is uncommon in the United States, but it can happen if you don’t get professional care for gum infections and diseases.
3. Swollen Gums May Mean Nutritional Deficiencies
Nutritional imbalance can impact oral health, so balanced dietary habits are essential. A balanced diet ensures you have the nutrients necessary for healthy oral mucosa and dental hard tissues.
Vitamin C deficiency interferes with your ability to maintain and repair your gums and teeth. It also makes you more likely to develop scurvy, a disorder that can cause gum disease and other complications.
Other nutritional deficiencies that can disrupt your oral health include:
- vitamins b, d, and k
- calcium
- magnesium
- fiber
- carbohydrates
- proteins
You should also consider limiting sugar, starchy or refined carbohydrates, and acidic items because they can disrupt oral health. Sugar triggers bacteria build-up and isn’t always easy for your saliva to rinse away, while carbohydrates become sugar during digestion. Acidic items aren’t ideal because they erode tooth enamel, increasing your risk of cavities.
Implementing dietary changes can make a difference in your oral health. It can help you heal your gums and reverse the effects of gum disease and other issues. You’ll have an easier time maintaining oral health with these beneficial nutritional changes.
4. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations can interfere with your gum health. Any changes to your hormonal balance can cause swelling, but pregnancy and menopause are leading contributors.
During pregnancy, you’ll experience increased hormones that can increase blood flow to your gums. If this occurs, you’re likely to experience swelling and sensitivity. Pregnant people also can’t fight bacteria as well, potentially triggering gum infections.
Menopause causes estrogen and progesterone fluctuations, both of which affect oral health. It can cause gum swelling, pain, and bleeding while contributing to bone loss in the jaw and bones surrounding your teeth. Fluctuating hormones can also decrease saliva production, making bacteria more likely to build up in your dry mouth.
5. Swollen Gums and Medication Side Effects
Research shows some medication side effects can cause gum swelling. Blood pressure drugs and oral contraceptives are two types that often cause this issue.
Other medications that commonly cause swollen gums include:
- anticonvulsants (medication to treat seizures)
- anticoagulants (prescribed to prevent heart attack and stroke)
- immunosuppressants (medication to prevent organ transplant rejection or to treat autoimmune disease)
- antidepressants (medication used to treat depression)
- antihistamines (allergy treatment)
- asthma medications
If you believe your swollen gums result from a medication reaction, talk to your doctor before stopping the medication. They can prescribe another medication that you don’t react to this way, allowing you to maintain your health. If you stop taking it without discussing it with your doctor, you can have other issues related to not taking your medication.
6. Allergic Reactions
Food allergies and hypersensitivity sometimes manifest as oral health reactions. It could cause red or white mucosa and swelling of your cheeks, tongue, and lips. Sometimes you’ll also experience ulcers and blisters, depending on the severity.
Seasonal allergies can also cause gum swelling from the post-nasal drip. If you think these things could be causing you issues, seeking medical care can help confirm it.
Taking antihistamines for allergic reactions can also contribute to dental issues as it reduces saliva production. If you take these medications, prioritize staying hydrated to avoid dry mouth.
7. Systemic Diseases
Systemic diseases, including diabetes, heart disease, and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) can cause swollen gums. Red, swollen, and bleeding gums are symptoms of diabetes, and you should seek help from a health professional immediately.
The same symptoms can also indicate heart disease. When bacteria infect your gums, they can travel to your blood vessels and cause them to become inflamed and damaged. Taking care of your teeth and gums can help alleviate your risk of heart issues.
Those with RA experience inflammation throughout the body, including on their gums. It also interferes with your immune response, so viruses and bacteria on your teeth can easily exacerbate swelling. However, if you have RA, bacteria don’t need to be present to experience swelling because inflammation gets triggered without foreign bodies.
Seeking Dental Evaluation for Swollen Gums
Consider seeking a dental consultation for persistent gum swelling. Call a dentist for treatment if it lasts a week or two. Your treatment options depend on the cause, so it’s best to receive a diagnosis instead of attempting to resolve the issue without help.
The sooner you seek professional help, the less likely the issue will worsen and cause pain. If you already have pain from the swelling, contact a professional immediately. Once you find a professional you’re comfortable with, schedule a professional cleaning and regular oral examinations.
While waiting for your upcoming appointment, you can do things at home to ease the symptoms. Consider rinsing your mouth with warm saltwater multiple times daily. Another option is to apply an ice pack to your face at the place of inflammation.

Final Thoughts on Swollen Gums and Health Implications
Swollen gums lasting longer than a week indicate an underlying issue. It could indicate gum disease, hormonal imbalances, nutrient deficiencies, health problems, and reactions.
Seeking dental evaluation for proper diagnosis and treatment is essential to your gum health. Addressing the underlying causes of gum inflammation is the only sure way to prevent it from worsening or returning.
Good oral health can help reverse and prevent swollen gums, but treatment is necessary first. Once the swelling eases, focus on eliminating detrimental dental habits and scheduling regular check-ups.