More than 12 percent of the U.S. population will develop a thyroid condition during their lifetime. – American Thyroid Association (ATA)
Facts About the Thyroid Gland
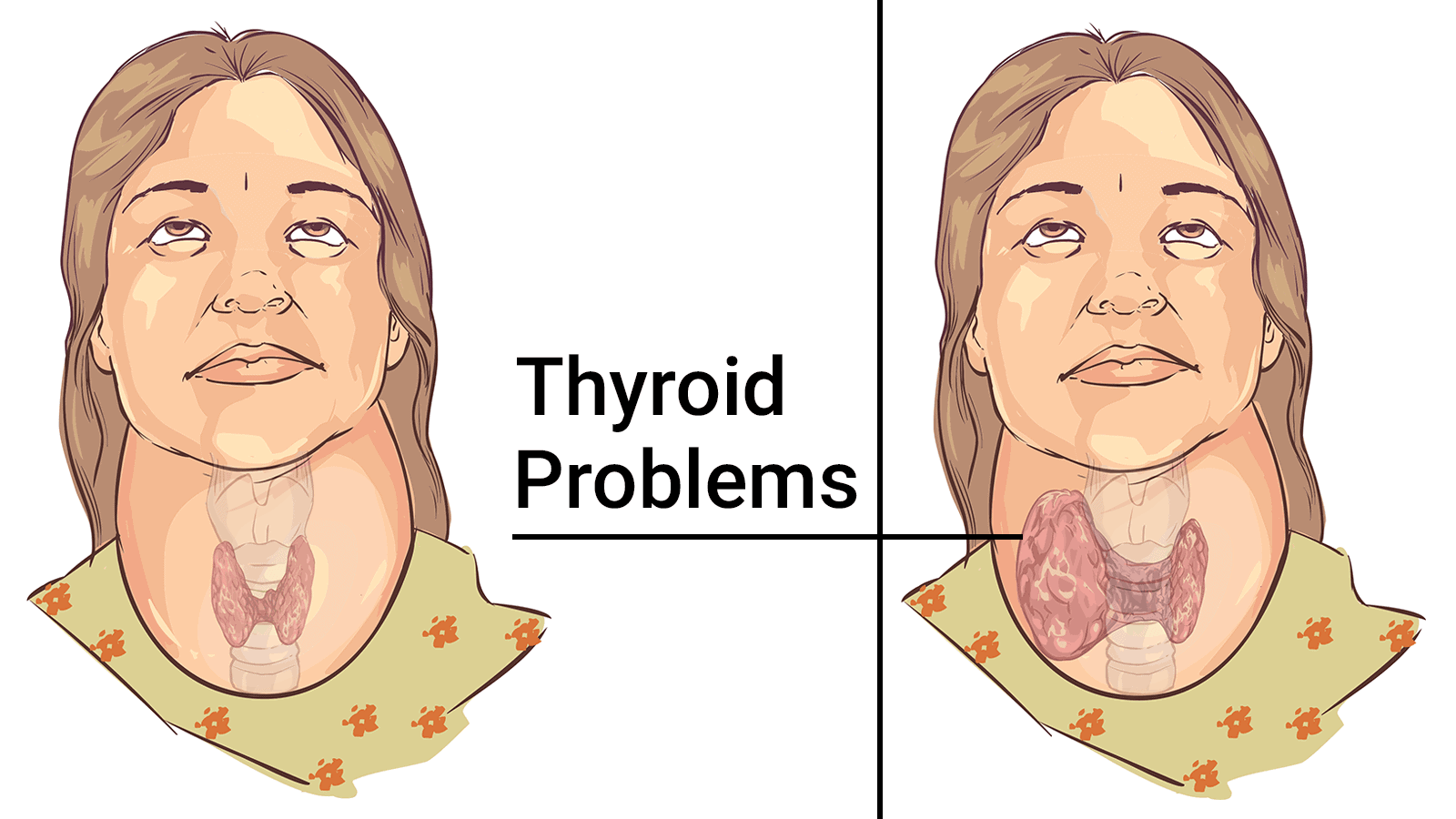
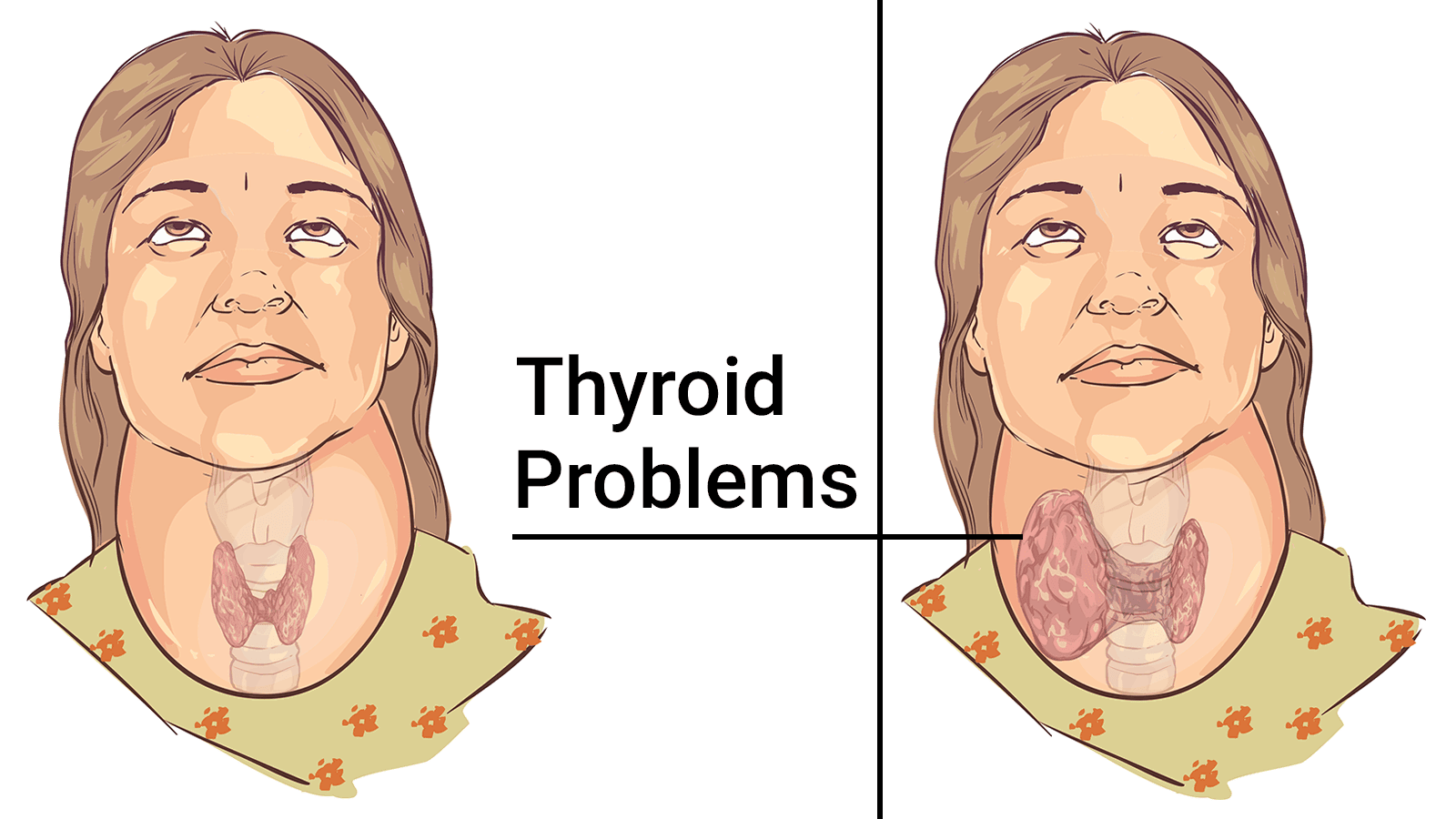
The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located in the middle of the lower neck that helps regulate metabolism (the rate at which your body uses energy from nutrients you eat and the oxygen you breathe), produce hormones, and affects body functions such as heart rate and energy levels. The thyroid produces two main hormones: triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4).
Though the thyroid gland is small, it is one of the most important glands in the body, as it affects every single cell, tissue, and organ in the body. As we said, many people develop conditions of this gland. We will go over the two main thyroid disorders below, with facts from the ATA.
Facts about Thyroid Diseases
- Hypothyroidism happens when this gland doesn’t produce enough thyroid hormone. Symptoms include forgetfulness, depression, fatigue, and weight gain.
- Hyperthyroidism, on the other hand, occurs when the body produces too much of its hormone. Symptoms include anxiety, irritability, insomnia, weight loss, eye irritation, and muscle weakness.
- Graves’ disease, a type of hyperthyroidism, is a genetic autoimmune disorder and is estimated to affect 1% of the population.
- Around 20 million Americans suffer from some type of thyroid disorder.
- Up to 60 percent of people with a thyroid disease don’t even know they have it.
- Women are at a higher risk of developing a thyroid disorder than men. Women develop them more than five to eight times more frequently than men.
- One in eight women will develop a disease involving this gland.
- Thyroid cancer responds well to treatment.
- Currently, the causes of thyroid disease are unknown.
- Undiagnosed and untreated conditions may put the person at risk of more serious diseases, such as cardiovascular disease, infertility, and osteoporosis.
- Pregnant women with undiagnosed or untreated hypothyroidism have a greater risk of miscarriage, premature delivery, and significant developmental problems in their children.
- While most thyroid diseases require life-long treatment, they can be managed well with the proper care.
Now that you know a little bit about the functions of this gland and related disorders, we will talk about the signs of a thyroid problem.
Signs of A Thyroid Disease
According to the Cleveland Clinic, here are the main signs of hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism:
Signs of Hyperthyroidism
Irritability/nervousness
When the body produces too much thyroid hormone, this causes the metabolism to run much faster than necessary. A person with hyperthyroidism may seem anxious or jittery for no reason, and will become irritated easily.
Muscle weakness or tremors
This usually presents as a slight shake in the hands and fingers. Again, this happens because the body is producing more thyroid hormone than necessary, leading to excess energy. When you have unused energy, your body will do whatever it can to rid itself of that energy.
Irregular, light menstrual cycles
If you have are a woman with this issue, you might notice that your periods are lighter, shorter, and occur infrequently. This is because having too little thyroid hormone production affects other hormones in the body, such as the thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), which has a direct effect on the ovary. Decreased levels of this hormone may lower prolactin levels, leading to irregular periods.
Weight loss
This is one of the most obvious signs of hyperthyroidism. If your thyroid is overactive, you’ll start losing weight unexpectedly due to a higher metabolism. Even if your appetite and exercise regimen remain the same, you will still experience weight loss.
Sleep problems
Because your nervous system is overstimulated, you may notice you have a harder time falling asleep at night. Even if you feel tired, your metabolism is still running high and may prevent you from falling and staying asleep. You may also experience night sweats, restlessness, and leg tremors.
Eye irritation or problems
This usually occurs in patients with Graves’ disease. Symptoms include feeling of irritation or grittiness in the eyes, redness or inflammation of the white part of the eyes, dry eyes, swelling of the eyelids, sensitivity to light, bulging of the eyes, and double vision.
Sensitivity to heat
People with hyperthyroidism will become hot easily due to excess thyroid hormones. Your metabolism increases, leading to a rise in body temperature.
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
Fatigue
If you feel exhausted all the time, even after getting adequate sleep, you might have hypothyroidism. Fatigue occurs because your body doesn’t produce enough thyroid hormone, which helps give you energy. Though fatigue can be a symptom of many different disorders, it’s worth getting checked out if you also have other symptoms on this list.
Weight gain/inability to lose weight
According to the American Thyroid Association, people with hypothyroidism generally present with weight gain or a hard time losing weight. However, in most people, only 5-10 pounds of weight gain is attributable to the underactive thyroid. Most of the excess weight gained by people with hypothyroidism is due to the accumulation of water and salt.
People with this condition have a low BMR (basal metabolic rate), which makes it much easier to gain weight. Low energy levels lead to less calories burned by the body, meaning that even eating a small amount can result in weight gain. Also, since the metabolism is damaged, those with this condition will have a hard time losing weight as well.
Depression
While research isn’t conclusive about the connection between depression and hypothyroidism, some people will experience feelings of depression who also have low thyroid hormone production. Some scientists speculate that patients might get depressed due to the other organs in the body slowing down, but more research needs to be done on this topic.
Forgetfulness and brain fog
As thyroid hormone production slows down, some people may experience brain fog, difficulty remembering things, or decreased awareness. This is because all the body’s organs slow down, including the brain. Without enough of this hormone, the body can’t efficiently send signals to the brain, leading to cognitive impairment.
Dry skin and brittle hair
Because hypothyroidism slows down the metabolism, this will cause you to sweat less, leading to dry hair, skin, and nails. Sweating helps to keep the skin and hair moist, so a lack of sweat can certainly cause a change in the skin’s texture and appearance.
Heavy menstrual cycles
In contrast to women with hyperthyroidism, women with an underactive thyroid often experience heavy periods. This is because without sufficient hormones from this gland, your ovaries may not be able to make enough of the hormone progesterone, which helps decrease blood flow. Also, your blood may not coagulate as well, which helps to prevent heavy bleeding. Thirdly, you make less of the estrogen-binding protein SHBG, which means your estrogen levels will be too high. All of this can lead to heavier menstrual cycles.
Sensitivity to cold
While people with hyperthyroidism are intolerant to heat, those with hypothyroidism have greater sensitivity to cold. This happens because the hormone this gland produces helps regulate body temperature, so when you don’t have enough of the hormone, you will feel cold more easily.
We’ve discussed the signs and symptoms of the most common types of thyroid disorder, so now, we’ll go over treatments for both conditions.
Treatment for Thyroid Disease
- Hyperthyroidism: For this condition, a doctor may prescribe antithyroid drugs that block the body’s ability to produce extra thyroid hormone. Alternatively, he might suggest beta-blockers which will lessen certain symptoms such as shakiness or nervousness, though they won’t lower the levels of this hormone in your body.
Your doctor may also suggest something called radioactive iodine, which has been used as a treatment for over 60 years in the U.S. and is still used today on 70% of patients with hyperthyroidism. Radioactive iodine is taken in the form of a small capsule, usually just once. It works by damaging or destroying overactive thyroid cells. As a last resort, the doctor may suggest surgery, though it usually isn’t necessary.
- Hypothyroidism: Currently, the only treatment for an underactive thyroid is taking the synthetic thyroid hormone levothyroxine daily. This medication will help bring your T4 and TSH levels back to normal, thus reversing symptoms of hypothyroidism such as fatigue. For patients who still don’t feel normal taking the synthetic T4 hormone alone, the doctor might supplement them with T3 to increase hormone levels.
How to Test Yourself for Thyroid Problems in 60 seconds
Check the pulse on the inside of your wrist using your first and second fingers. Count the beats of your pulse for one minute. Do this in the morning for three days. If the pulse is consistent each day, your thyroid is functioning normally. If there are inconsistencies, it might point to a problem.
Final thoughts
We hope you have learned valuable information about the thyroid gland and related disorders. If you have a concern, make sure to get checked by a doctor as soon as possible.
No matter if you have an underactive or overactive thyroid, there are adequate treatments available for each condition. The most important thing is to seek help before the condition becomes unmanageable.