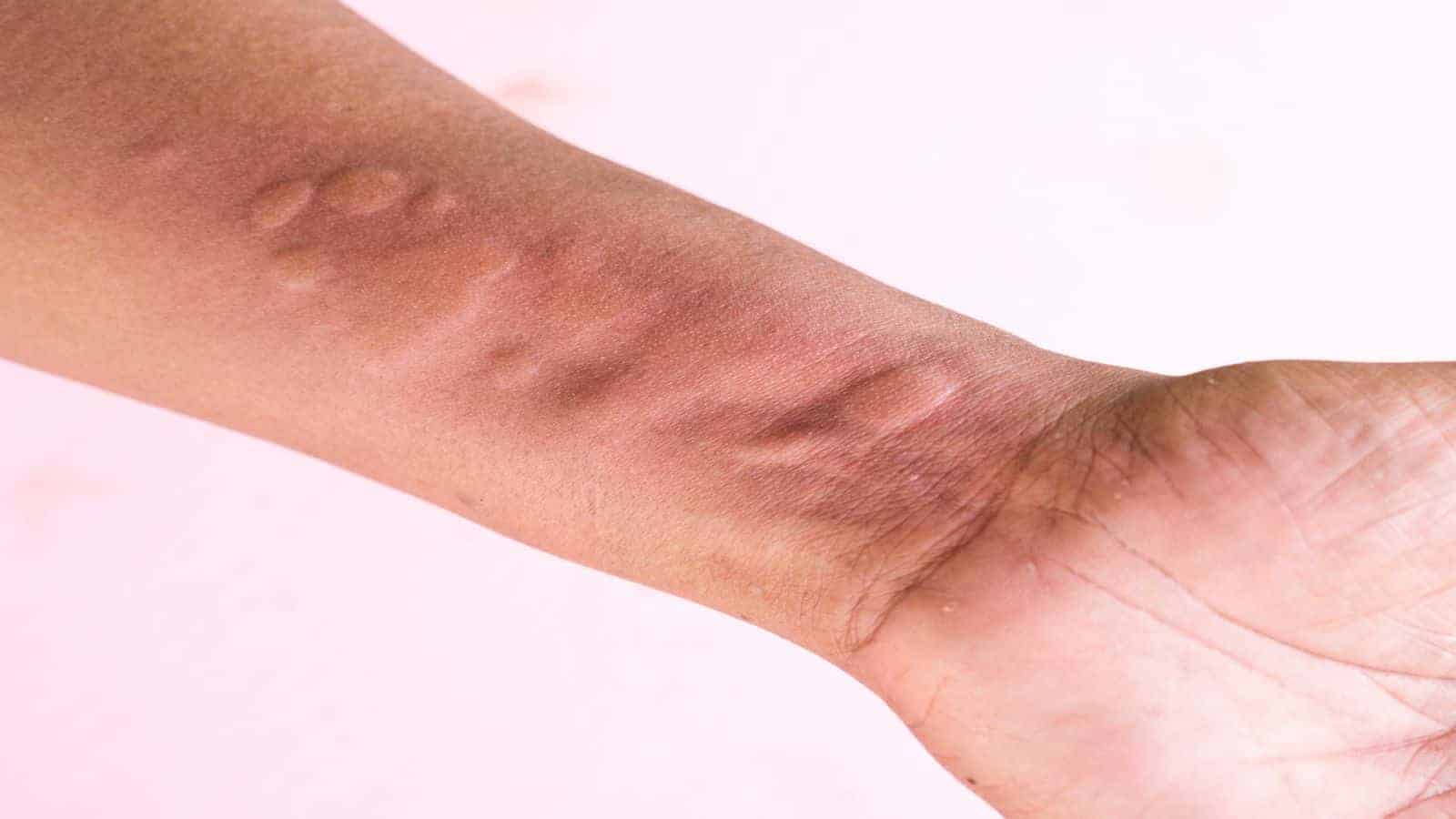
Have you ever experienced hives? They are an itchy skin rash that is frequently caused by an allergic reaction. The medical community calls this condition nettle rash, welts, or urticaria.
People experience this problem commonly. Indeed, statistics indicate that approximately twenty percent of the population will deal with this condition at least once.
When you see hives on your body, it’s due to the production of histamine. What is histamine? Well, it’s something that your body produces to let you know that you’re having an allergy response to a foreign invader. Histamine is a protein that is leaked from the capillaries. These capillaries swell and accumulate under the skin, which causes the raised places known as hives. Thankfully, this unsightly rash is not contagious.
Triggers of Hives
Many different things can cause urticaria to occur. An acute case would be something that happens once with no known reason. A chronic case is one where this rash keeps appearing.
It may take your doctor some time to pinpoint the exact cause of your allergic response. For most people, a cause is never identified. Here are the most common reasons for developing hives, according to science.
- Intestinal Parasites
- Fevers
- Dust Mites
- Medications
- Food Allergies– Specifically Shellfish or Nuts
- Viral Infection
- Bacterial Infection
- Changes in Body Temperature
- Fevers
- Intestinal Parasites
- Pet Dander
- Pollen
- Poisonous Plants – Poison Ivy, Sumac, or Oak
- Waste from Cockroaches
- Insect Sting or Bite
- Excessive Scratching
- Thyroid Disease
- Lupus
- Latex Products
- Chemicals
- Being in the Sun
- Exercise
How to Identify Hives
Hives cause welts or a swelling that looks like a typical rash on your skin. The color is usually pink or red, and the bumps are an oval shape. The welts can be small or up to several inches in size, and it all depends on your immune response as to how big they get.
The most common problem with these bumps is that they’re itchy, and they can become red and inflamed. Like a classic rash, the spots will occur in batches. They are often found on the face or extremities of the body.
It’s normal for the welts to disappear within a day; however, new ones will form to take their place. Some people will have the rash localized to one area, while others will have them in many different places. When the condition is chronic, the welts can last for months or even years.
The Three Types of Hives
Urticaria can be acute or chronic, and it’s important to distinguish between those two and angioedema. The timeline is used to help diagnose your condition. Anything that doesn’t resolve itself within a couple of weeks is said to be chronic. Here are some facts to help you understand the three types of urticaria.
• Acute
Acute is the most common variety of urticaria. You will see the rash on the neck, face, genitals, toes, and fingers. Sadly, any part of the body can be affected, not just the typical hotspots. The duration is under six weeks to be considered acute.
• Chronic
Chronic hives plague about one percent of the population, and it’s a condition that can last for up to six weeks. Sadly, some complications can arise in addition to long-term pain and discomfort. Treatment methods for this type of urticaria are different than the acute variety.
It’s believed that this chronic condition begins as an autoimmune response; however, the reasons that it occurs is still unclear. The occurrences are higher in people who suffer from conditions like lupus and thyroid disease.
• Angioedema
Angioedema is remarkably like urticaria, but the swelling is much deeper and more pronounced. Usually, the swelling resolves within 24 hours, though the condition may linger for weeks.
An allergist can help patients with this condition as it can create serious, potentially life-threatening complications. An immunologist may also be able to help. Since angioedema often occurs with swelling of the tongue or lips, patients need to carry a fast-acting medication like an EpiPen with them.
After a few bouts of these hives, it’s easier to pinpoint what’s causing the allergic response.
Making a Diagnosis
Making a diagnosis is not difficult, as most doctors are quite familiar with this condition. They will examine the rash and ask questions about when the episode began. Things like an insect bite, wearing latex gloves, or eating something new can be a trigger.
Your medical team will also need to know if you’ve had issues with these in the past. Allergy testing is possible if you continue to have problems with hives. When the condition has been consistent for more than six weeks, they will want to do further examinations.
Routine blood tests will look for parasites and anemia, as well as any other probable causes. Another test that is commonly used is the SED rate or ESR test. A high level of inflammation in the body will identify a problem with the immune system.
An underlying issue like thyroid disease, lupus, or liver problems is to blame in many cases. Though a doctor can diagnose by sight, they may want to dig a bit deeper into why this keeps occurring.
How Doctors Might Treat Hives
In the mildest cases, you can treat the itching at home with a remedy like a baking soda paste or calamine lotion. But severe cases might require a trip to the doctor. Most notably, anaphylaxis, a severe allergic reaction, can also involve hives, and you must report to the emergency room without hesitation.
• Antihistamines
Using antihistamine medications is a favored treatment method as it blocks the histamine and helps relieve the itching caused by the rash. The real issue with antihistamine products is the fact that they’re sedating. It’s hard to take these medications while working because they cause drowsiness.
• Steroids
Another standard method used is steroids. Steroids help reduce inflammation and help cases where the breathing is labored from an allergic reaction. A significant issue with long term steroid use is moon face and mood disturbances as well as insomnia.
• Supplements
Nature provides many supplements that can help to build the immune system to ward off such responses. The most used in these situations include Vitamins C and D as well as primrose oil.
While natural supplements are safe, they can counteract with medications and trigger adverse reactions. It’s important to talk to your doctor before mixing supplements and prescriptions.
• Acupuncture
Acupuncture is an ancient art that has become popular in America. A study shows that it may be an effective and safe treatment for hives, especially those who suffer from the chronic version. By stimulating specific trigger points in the body, it can help to improve the reaction to allergens.
• Diet Modification
Many people find that keeping a food journal is helpful. When you find the foods that trigger a response, then you can avoid them. Some foods are more likely to cause histamine production than others. These foods include:
- Fish
- Yogurt
- Processed Meat
- Chocolate
- Nuts
- Strawberries
- Spinach
- Tomatoes
How Stress Plays a Part in Urticaria
Being under severe stress for long periods can have a devastating effect on the body. A study was conducted in 2005 that examined how stressful events in life and the lack of family support resulted in urticaria for 75 people.
When your body is under duress, it can aggravate an underlying condition. Your body’s natural defenses are an inflammatory reaction, and it can be more severe in a person under a great deal of distress.
In people who aren’t under such turmoil, their bodies can fight off the condition, and it might not be as severe. However, when someone is under great duress, then the cortisol and adrenaline levels are too high. These hormones help to keep things balanced.
When parts of your system are misfunctioning, it can cause other issues in the body.
 Final Thoughts on Dealing with Hives
Final Thoughts on Dealing with Hives
There are many things that you can do to help ease the discomfort that comes with urticaria. Some things that can help include wearing loose clothing that won’t rub and further irritate the area. Something light that won’t make you overheated is also advisable.
Whatever you do, try not to scratch the area. You can use things like calamine lotion to remove the itch caused by the histamines in the skin. You don’t want to further irritate the site by using perfumed soaps, so try to stick with an all-natural soap meant for sensitive skin.
If you’ve scratched the area and it’s become severely inflamed, then you can try a cold shower and sitting in front of a fan to help. Also, a cool compress may help to alleviate the discomfort you feel. Many have found that taking an oatmeal bath with tepid water helps to soothe their skin.
Remember, hot water will only further irritate and hurt the area.
Lastly, it’s essential to know your triggers, especially if this becomes a common occurrence. The more facts you have for your doctor, the easier it’s to pinpoint the reasons behind this painful problem. And if you have other symptoms that could indicate a life-threatening allergy, go to the emergency department right away.